36
English
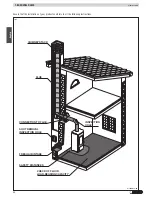
1.5 Installation environment
The appliance should be installed in a location which allows safe and convenient use as well as easy maintenance. If the product being installed
requires an electrical socket, the room must also be provided with an earthed power supply in accordance with current regulations.
The room where the appliance is to be installed or adjoining rooms must comply with the following requirements.
The installation of a wood-burning appliance in a bedroom, bath or shower room or in any room where another heating system not
equipped with its own air supply (fireplace, stove etc.) has already been installed is forbidden.
They must not be used as a garage, store for combustible material or for activities with a risk of fire.
They must not be in a vacuum in relation to the outside environment due to the effect of contrary draught caused by the presence
in the room where the stove is installed of another appliance or an extractor device.
Do not use two stoves, a fireplace and a stove, a stove and a wood-fired cooking range, etc. in the same environment, since the
draught of one could affect the draught of the other.
- Devices suitable for cooking food with relative hoods without an extractor fan may only be used in kitchens.
- Gas appliances of type C are allowed (refer to current legislation and regulations in the place of installation)
Gas appliances of type B are not allowed (refer to current legislation and regulations in the place of installation)
The stove or fireplace must not be used simultaneously with collective type ventilation ducts with or without extractor fan, other
devices or other appliances such as: forced ventilation systems or other heating systems using ventilation to change the air. Such
systems could cause a vacuum in the environment of installation even if installed in adjoining or communicating rooms.
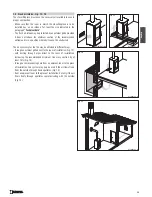
1.6 Capacity load of the floor
Check the load-bearing capacity of the floor, referring to the weight of the product given in the paragraph
“Technical data”
.
If the floor does not have a suitable load-bearing capacity, adequate countermeasures must be taken, for example, by using a sheet metal
plate to distribute the load.
1.7 Heating capacity
Check the heating capacity of the appliance by comparing the rated power given in the paragraph
“Technical data”
with the power required
by the environment to be heated.
The energy requirement may be calculated approximately by multiplying the square metres of area by the height of the ceiling; the result
is then multiplied by a coefficient, which depends on the degree of insulation of the building, that is, on internal and external factors of
the dwelling:
a)
Internal factors:
type of window and door frames, thickness of the insulation and walls, type of building materials, presence of
stairwells, walls with extensive glazing, high ceilings, position of the rooms to be heated in relation to other adjacent heated or
unheated rooms, …
b)
External factors:
geographical position, average outdoor temperature, exposure, wind speed, latitude, altitude, …
Example of approximate calculation of the energy requirement to heat a fixed volume to 18/20° C:
The
coefficient
that is normally
used
is determined according to the real conditions as they occur case by case.
- From
0.04
to
0.05 kW
per cubic metre in a
well insulated environment
- From
0.05
to
0.06 kW
per cubic metre in a
poorly insulated environment
3 rooms measuring 20m2 X (H ceiling) 2.7m = 162 m
3
(volume)
In an environment with a good degree of insulation, an average value (coefficient) of 0.045 kW may be taken
162 (volume) X 0.045 (kW) = 7.3 kW necessary (6300 kcal/h)
Conversion 1kW = 860 kcal/h
Consult a heating technician or engineer for a correct check and calculation of the requirement of the environments to be heated
(see “Reference standards”).
Rated power being equal, products with the Multi-fire system can evenly distribute heat throughout the rooms to be heated.