4
TH-50VX100U / TH-50VX100E
2 Warning
2.1.
Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatically Sensi-
tive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called Elec-
trostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as alumi-
num foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static (ESD protected)” can
generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or compara-
ble conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise ham less motion such as the brush-
ing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficient
to damage an ES device).
Summary of Contents for TH-50VX100U
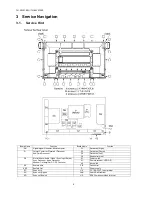
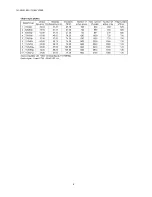
Page 7: ...7 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 3 2 Applicable signals...
Page 8: ...8 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E...
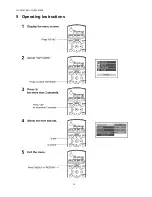
Page 10: ...10 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 5 Operating Instructions...
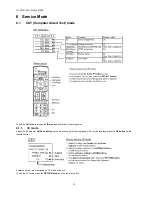
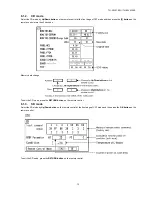
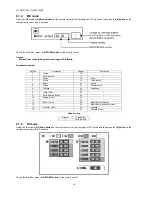
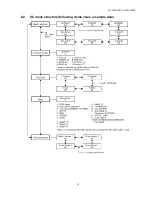
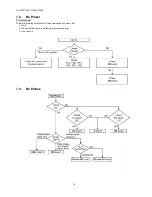
Page 15: ...15 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 6 2 IIC mode structure following items value is sample data...
Page 33: ...33 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 9 1 4 Adjustment Volume Location 9 1 5 Test Point Location...
Page 35: ...35 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E...
Page 37: ...37 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E...
Page 38: ...38 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E...
Page 47: ...47 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 11 Wiring Connection Diagram 11 1 Wiring 1...
Page 48: ...48 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 11 2 Wiring 2...
Page 49: ...49 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 11 3 Wiring 3...
Page 50: ...50 TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E...
Page 51: ...TH 50VX100U TH 50VX100E 51 12 Schematic Diagram 12 1 Schematic Diagram Notes...
Page 169: ...Model No TH 50VX100U E Exploded View...
Page 170: ...Model No TH 50VX100U E Cabinet part location...
Page 171: ...Model No TH 50VX100U E Fan part location...
Page 172: ...Model No TH 50VX100U E Flat cable...
Page 173: ...Model No TH 50VX100U E Accessories...
Page 174: ...Model No TH 50VX100U E Packing 1...
Page 175: ...Model No TH 50VX100U E Packing 2...