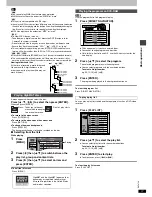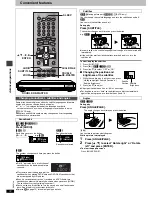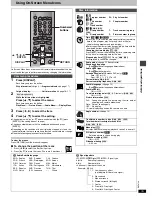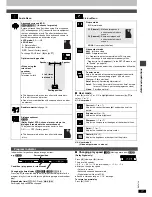
C
2003 Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd.
Printed in Singapore
RQT6726-P
F1202FM0
Glossary
Bitstream
The digital form of multi-channel data (e.g.
5.1 channel) before decoding.
Decoder
A decoder restores coded audio signals on
DVDs to normal.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals
developed by Dolby Laboratories. Apart from
stereo (2-channel) audio, these signals can also
be multi-channel audio. A large amount of audio
information can be recorded on one disc using
this method.
Dolby Pro Logic
A surround system where a 4-channel audio
track is recorded as 2 channels and then is
restored to 4 channels for play. The surround
channel is monaural and can reproduce up to
7 kHz.
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie
theaters around the world. There is good
separation between the channels, so realistic
sound effects are possible.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the
lowest level of sound that can be heard above
the noise of the equipment and the highest level
of sound before distortion occurs.
Film and video
DVD-Videos are recorded using either film or
video. Usually, film is recorded at 24 frames per
second, the rate movies are filmed at, while
video is recorded at 30 frames per second.
Frame still and field still
Frames are the still pictures that make moving
pictures. About thirty are shown each second. A
frame still may appear blurred but overall quality
is high.
Two fields appear alternately to make up one
frame. A field still is not blurred but picture
quality is lower.
Interlace and progressive output
NTSC, the video signal standard, has 480
interlaced (I) scan lines, whereas progressive
scanning uses twice the number of scan lines.
This is called 480P.
I/P/B
MPEG 2, the video compression standard
adopted for use with DVD-Video, codes frames
using these 3 picture types.
I:
Intra coded picture
This picture has the best quality and is the
best to use when adjusting the picture.
P:
Predictive coded picture
This picture is calculated based on past I or
P-pictures.
B:
Bidirectionally-predictive coded picture
This picture is calculated by comparing
past and future I and P-pictures so it has
the lowest volume of information.
Linear PCM (pulse code modulation)
These are uncompressed digital signals, similar
to those found on CDs.
Signal system:
[For\U.S.A.\and\Canada]
:
NTSC
[For\others]
:
PAL 625/50, PAL525/60, NTSC
Operating temperature range:
i
5 to
i
35
o
C (
i
41 to
i
95
o
F)
Operating humidity range:
5 to 90 % RH (no condensation)
Discs played [8 cm (3
z
) or 12 cm (5
z
)]:
(1) DVD-RAM (DVD-VR compatible)
(2) DVD-Audio
(3) DVD-Video
(4) DVD-R (DVD-Video compatible)
(5) CD-Audio (CD-DA)
(6) Video CD
(7) SVCD (Conforming to IEC62107)
(8) CD-R/CD-RW
(CD-DA, Video-CD formatted discs)
(9) MP3/WMA
§
≥
Maximum number of tracks and groups
recognizable: 999 tracks and 99
groups
≥
Compatible compression rate:
MP3: between 32 kbps and 320 kbps
WMA
§
: between 48 kbps and 192 kbps
(10) JPEG
§
≥
Exif Ver 2.1 JPEG Baseline files
≥
Maximum number of pictures and
groups recognizable:
3000 pictures and 300 groups
≥
Picture resolution:
between 320
t
240 and 6144
t
4096 pixels (Sub sampling is 4:2:2 or
4:2:0)
(11) HighMAT Level 2 (Audio and Image)
Video output:
Output level:
1 Vp-p (75
≠
)
Output terminal:
Pin jack (1 system)
S-video output:
Y output level:
1 Vp-p (75
≠
)
C output level:
[For\U.S.A.\and\Canada]
NTSC; 0.286 Vp-p (75
≠
)
[For\others\
NTSC; 0.286 Vp-p (75
≠
)
PAL; 0.300 Vp-p (75
≠
)
Output terminal;
S terminal (1 system)
Component video output:
[For\U.S.A.\and\Canada]
;
(480P/480I)
[For\others\]
(NTSC: 480P/480I, PAL: 576I)
Y output level:
1 Vp-p (75
≠
)
P
B
output level:
0.7 Vp-p (75
≠
)
P
R
output level:
0.7 Vp-p (75
≠
)
Output terminal:
Pin jack
(1 system, Y: green, P
B
: blue, P
R
: red)
Audio output:
Output level:
2 Vrms (1 kHz, 0 dB)
Output terminal:
Pin jack
Number of terminals: 2 channel:1 system
Audio performance:
(1) Frequency response:
≥
DVD (linear audio):
4 Hz–22 kHz (48 kHz sampling)
4 Hz–44 kHz (96 kHz sampling)
≥
DVD-Audio:
4 Hz–88 kHz (192 kHz sampling)
≥
CD audio:
4 Hz–20 kHz
(2) S/N ratio:
≥
CD audio:
115 dB
(3) Dynamic range:
≥
DVD (linear audio):
102 dB
≥
CD audio:
98 dB
(4) Total harmonic distortion:
≥
CD audio:
0.0025 %
Digital audio output:
Optical digital output:
Optical terminal
Pickup:
Wave length:
658 nm/790 nm
Laser power:
[For\U.S.A.\and\Canada]
CLASS
II
a/CLASS
I
[For\others]
CLASS 2/CLASS 1
Power supply:
[For\U.S.A.\and\Canada\
AC 120 V, 60 Hz
[For\Australia\and\N.Z.]
AC 220–240 V, 50 Hz
[For\Asia]
AC 220–240 V, 50/60 Hz
Power consumption:
15 W
Dimensions: 430 (W)
k
405 (D)
k
59.7 (H) mm
[16
15
/
16
z
(W)
k
15
31
/
32
z
(D)
k
2
11
/
32
z
(H)]
Mass:
4.1 k
g
(9.02 lb.)
Power consumption in standby mode:
[For\U.S.A.\and\Canada\
approx. 0.6 W
[For\others]
approx. 2.8 W
[Note]
Specifications are subject to change without
notice. Mass and dimensions are approximate.
§
DVD-F61 is not compatible with WMA, JPEG,
or HighMAT. References to them apply only to
DVD-F65.
Specifications
[For\U.S.A.]
Panasonic Consumer Electronics
Company, Division of Matsushita
Electric Corporation of America
One Panasonic Way Secaucus,
New Jersey 07094
http://www.panasonic.com
Panasonic Sales Company,
Division of Matsushita Electric of
Puerto Rico, Inc. (“PSC”)
Ave. 65 de Infantería, Km. 9.5
San Gabriel Industrial Park, Carolina,
Puerto Rico 00985
[For\Canada]
Panasonic Canada Inc.
5770 Ambler Drive
Mississauga, Ontario
L4W 2T3
www.panasonic.ca
pr
[For\others]
Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd.
Web Site: http://www.panasonic.co.jp/global/