Page 51
TU2506
ǀ
TU2807V
US
Note that the diameter of the drill and not the workpiece was used for RPM calculation. This
was done because the cutting takes place at the diameter of the drill, not on the outside diame-
ter of the workpiece.
A turning operation is to be done on a 3.00-inch piece of 4140-alloy steel with a hardness of
200 HB. A carbide turning tool is to be used. Calculate the RPM setting to perform this cut.
Cutting Speed = 400 fpm
Diameter of part = 3”
4.18.1 Selecting Feed per Revolution
There are three factors that make up cutting conditions; cutting speed, depth of cut, and feed
rate. The feed rate for turning is given in terms of inches per revolution (IPR). Inches per revolu-
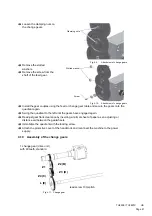
tion is the rate at which the tool will advance for every revolution of the workpiece Fig.4-20:
„Feed per revolution“ auf Seite 51. The feed rate is determined by the size of the chip that the
tool can withstand. The feed rate in inches per tooth is also known as chip load. Because turn-
ing tools have only one cutting edge, the chip load is expressed as inch per revolution.
Fig.4-20: Feed per revolution
The recommended values for chip load are based on the cutting tool material and the hardness
or machinability rating of the workpiece material. The recommended values for IPR (chip load)
can be found in charts in the Machinery's Handbook and charts given to you by your turning
tool salesperson. A typical feed in inches per revolution is shown
Rate Selection in Inches Per Revolution for Turning“ on page 52.
RPM =
Cs x 4
D
=
400 x 4
3
=
1600
3
= 533 RPM
Feed Per
Revolution
Feed
Direction
Summary of Contents for TU 2506
Page 1: ...US Item No 9684509 Operating manual Version 2 2 2 Lathe...
Page 74: ...Page 74 TU2506 US...
Page 92: ...Page 92 TU2506 TU2807V US 8 Wiring diagrams 8 1 TU2506 Fig 8 1 Wiring diagram TU2506...
Page 93: ...Page 93 TU2506 TU2807V US 8 2 TU2807V 230V Fig 8 2 Wiring diagram TU2807V...
Page 98: ...Page 98 TU2506 TU2807V US...