74
English
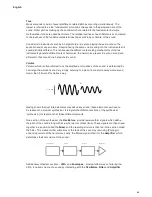
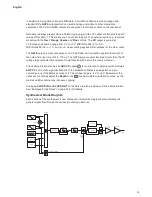
Oscillator Sync
Oscillator Sync is a commonly used technique of sound modification which you are likely to be
familiar with if you are already a synth user. On Circuit Mono Station, Oscillator Sync is enabled
by pressing
Osc 2
5
while holding
Shift
15
down. Oscillator Sync is a technique of using
one oscillator (Osc 1 on Circuit Mono Station) to add additional harmonics to the waveform
produced another (Osc 2), by making the waveform from Osc 1 “retrigger” that of Osc 2 before
a full cycle of Osc 2’s waveform has been completed. This produces an interesting range
of sonic effects, the nature of which varies as the frequency of Osc 1 is altered, and is also
dependent on the ratio of the two oscillators’ frequencies, as the additional harmonics may or
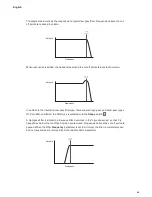
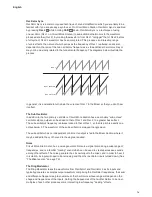
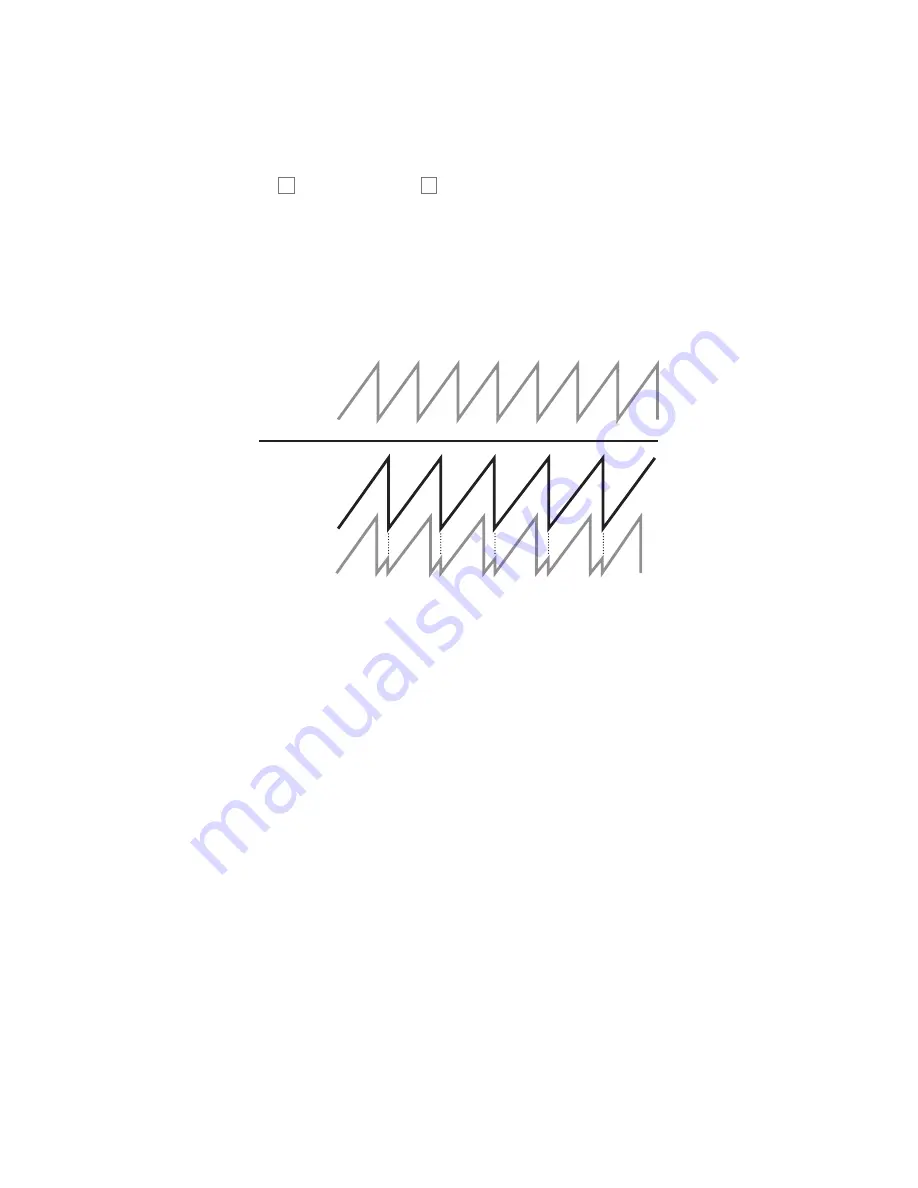
may not be musically related to the fundamental frequency. The diagrams below illustrate the
process.
OSC 2
OSC 1 (MASTER)
OSC 2 (SLAVE)
In general, it is advisable to turn down the volume of Osc 1 in the Mixer so that you don’t hear
its effect.
The Sub Oscillator
In addition to the two primary oscillators, Circuit Mono Station has a secondary “sub-octave”
oscillator, whose output can be added to that of Osc 1 and Osc 2 to a greater bass effect.
The sub oscillator’s frequency is always locked to that of Osc 1, so that its pitch is exactly one
octave below it. The waveform of the sub oscillator is always a triangle wave.
The sub oscillator has no independent controls. Its output is fed to the Mixer Section where it
may be added to the synth sound to the degree required.
Noise
Circuit Mono Station also has a noise generator. Noise is a signal comprising a wide range of
frequencies, and is a familiar “hissing” sound which can be used to create percussive sounds
among other effects. The noise generator has its own input to the mixer, and in order to hear it
in isolation, its input will need to be turned up and the other oscillator inputs turned down. (See
“The Mixer section” on page 75.)
The Ring Modulator
The Ring Modulator takes the waveforms from Oscillator1 and Oscillator 2 as its inputs and
typically generates a complex output waveform comprising the Oscillator frequencies, their sum
and difference frequencies, plus numerous other harmonics whose range will depend on the
shape and frequencies of the inputs. Setting the frequencies of the two Oscillators to be near-
multiples of each other produces some interesting low-frequency “beating” effects.
Summary of Contents for Circuit Mono Station
Page 1: ......
Page 93: ...93 English...