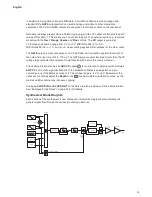
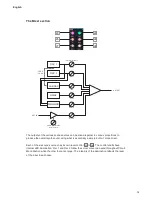
62
English
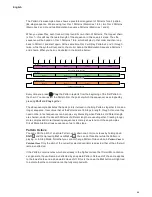
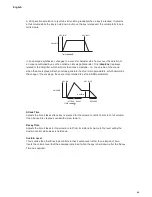
Triangle Waves
Volume
Harmonic
1
Sine Wave
Sawtooth Wave
Volume
Volume
Harmonic
Square Wave
Volume
Harmonic
1
2
3
4
5
Volume
Harmonic
1
3
5
7
Triangle Wave
1
2
3
4
5
Harmonic
1
2
3
4
5
Noise
These contain only odd harmonics. The volume of each decreases as the square of its position
in the harmonic series. For example, the 5th harmonic has a volume 1/25th of the volume of the
fundamental.
Sawtooth Waves
Volume
Harmonic
1
Sine Wave
Sawtooth Wave
Volume
Volume
Harmonic
Square Wave
Volume
Harmonic
1
2
3
4
5
Volume
Harmonic
1
3
5
7
Triangle Wave
1
2
3
4
5
Harmonic
1
2
3
4
5
Noise
These are rich in harmonics, and contain both even and odd harmonics of the fundamental
frequency. The volume of each is inversely proportional to its position in the harmonic series.
Square / Pulse Waves
Volume
Harmonic
1
Sine Wave
Sawtooth Wave
Volume
Volume
Harmonic
Square Wave
Volume
Harmonic
1
2
3
4
5
Volume
Harmonic
1
3
5
7
Triangle Wave
1
2
3
4
5
Harmonic
1
2
3
4
5
Noise
These contain only odd harmonics, which are at the same volume as the odd harmonics in a
sawtooth wave.
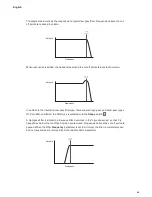
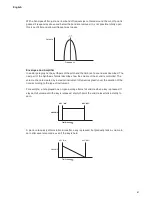
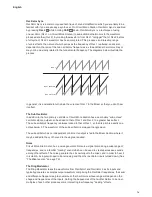
It will be noticed that the square waveform spends an equal amount of time in its ‘high’ state
as in its ‘low’ state. This ratio is known as the ‘duty cycle’. A square wave always has a duty
cycle of 50% which means it is ‘high’ for half the cycle and ‘low’ for the other half. Circuit Mono
Station lets you vary the duty cycle of the basic square waveform (via the Modulation Matrix) to
produce a waveform which may be more ‘rectangular’ in shape for part of the note’s duration.
Such waves are often known as Pulse waveforms. As the waveform becomes more and more
rectangular, more even harmonics are introduced and the waveform changes its character,
becoming more ‘nasal’ sounding.
Summary of Contents for Circuit Mono Station
Page 1: ......
Page 93: ...93 English...