Copyright © NetPing east Co., Ltd E-mail:
Phone:+886-2-23121582
[ENG] 10.2. [DKSF 48.4 IU] How to Use the Module «Logic»?
Rules allow to set a flexible logic scheme for controlling IO lines, relays, IR extension module, smoke sensors and sending SNMP SET commands
depending on altering external conditions.
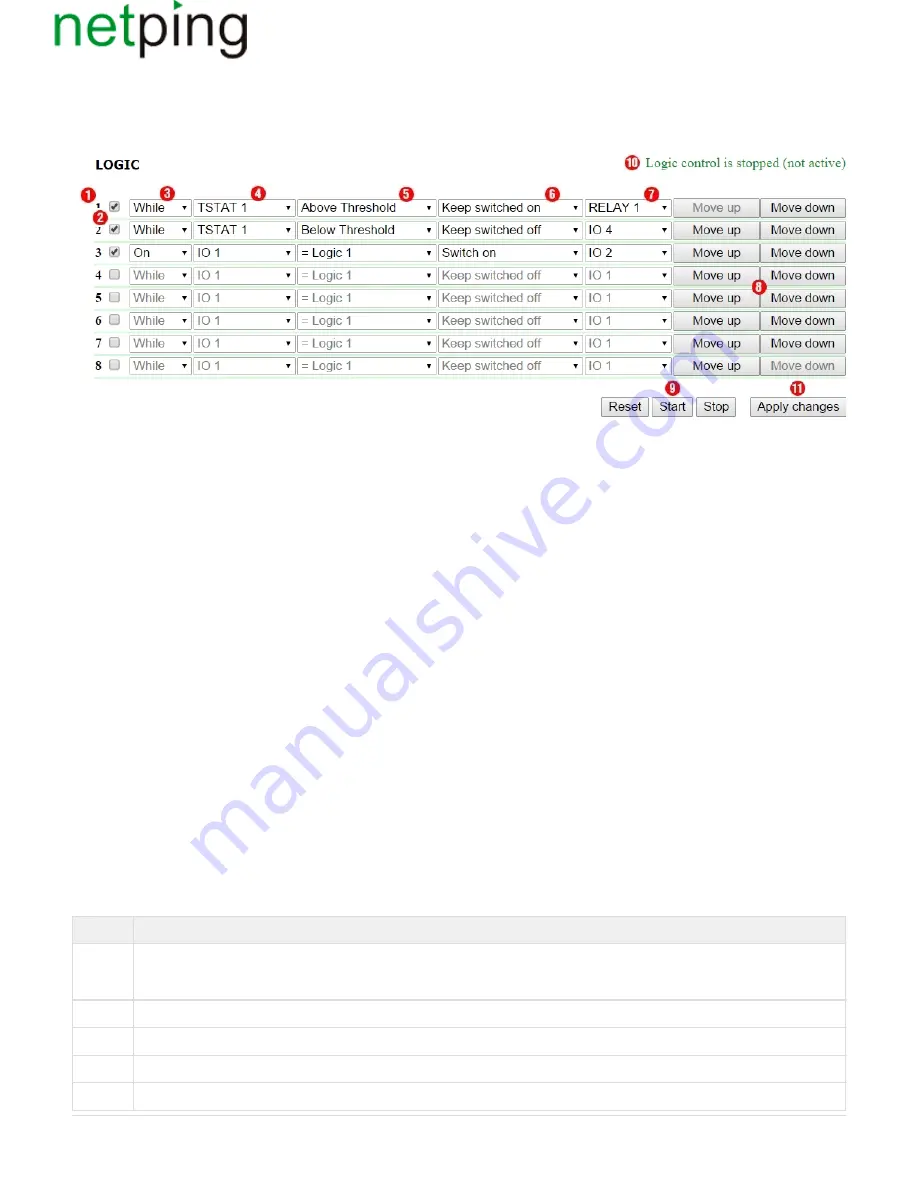
1. Rule Number
The less is a number of a line, the higher is a rule's priority. If two rules form a conflicting outgoing command (switch on and switch off an output
simultaneously), a rule with a higher priority will work. If rules do not conflict, and control different outputs or form non-conflicting commands then a
correlation of their priorities does not influence their operation.
Rules of «
» type always have a higher priority in relation to rules of « » type, regardless their mutual location in the list.
While
If
A priority of a rule (its position in the list) can be changed by using buttons « » («
» and «
») at the end of the line.
8
Move up
Move down
2. Checkbox for Enabling a Rule
A rule can be enabled by checking a checkbox. Inactive rules are displayed in gray.
3. Rule Type (Rule Operation Mode)
Possible values are: «While», «If». «While» rules respond to a status of an input and operate constantly. «If» rules respond to changes in a status of an
input (the second position in the rule line).
«While» rule is designed to program conditions, within which an output is constantly kept in a specified status while a condition is fulfilled. When a
condition is not fulfilled, an output status can be changed by other rules.
An «If» rule is designed to program a momentary reaction to a specified event, such as changing of a logic level at an IO line or losing a response when
Pinger works. When an input of a rule remains unchanged, an «If» rule does not influence a status of its output, even if a condition of a rule is fulfilled.
«
» rules always have a
, than « » rules.
While
higher priority
If
For example, when one of «While» rules keeps an output switched off, rules of «If» type, which switch on an output on a specified event, will not work.
4. Input
An input is a source of information for a rule operation. Its possible values are represented in the table:
Marking
Explanation
RESET
It is a signal, which is active 5 seconds after a module «
» has started or a module «
» has been reset using the button «
» at
Logic
Logic
Reset
the web page. It is used for a hardware initialization. For example, it is possible to program a 5-second pulse at a relay when a logic is
started or issue an IR command for switching a device off
IO 1
IO line 1. I
efore using
t must be set to the mode «input» at the page «INPUT-OUTPUT» b
IO 2
IO line 2. It must be set to the mode «input» at the page «INPUT-OUTPUT» before using
IO 3
IO line 3. It must be set to the mode «input» at the page «INPUT-OUTPUT» before using
IO 4
IO line 4. It must be set to the mode «input» at the page «INPUT-OUTPUT» before using














































