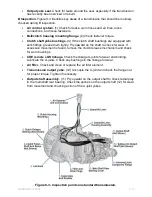
sure that you have some evidence that the cause is in the transmission before removing
it from the chassis.
Whining.
Gear whine is usually caused by insufficient backlash between mating gears,
such as improper shimming of a PTO. A high-pitched whine or squeal can also be
caused by mismatched gear sets. Such gear sets are identified by an uneven wear
pattern on the face of the gear teeth. Pinched bearings with insufficient axial or radial
clearance can also produce a whine.
Noise in neutral.
Possible causes of noise while the transmission is in neutral include:
•
Misalignment of transmission
•
Worn or seized flywheel pilot bearing
•
Worn or scored countershaft bearings
•
Worn or rough reverse idler gear
•
Sprung or worn countershaft
•
Excessive backlash in gears
•
Worn mainshaft pilot bearing
•
Scuffed gear tooth contact surface
•
Insufficient lubrication
•
Use of incorrect grade of lubricant
Noise in gear.
Possible causes of noise while the transmission is in gear include:
•
Worn or damaged mainshaft rear bearing
•
Rough, chipped, or tapered sliding gear teeth
•
Noisy speedometer gears
•
Excessive end play of mainshaft gears
•
Most of the conditions that can cause noise in neutral
Difficult to shift.
Difficult to shift is a condition that occurs when the shift lever is difficult
to move from gear to gear. In some instances, only one gear is hard to select; in others,
all shifting may be difficult.
The usual causes of hard shifting are bent or worn shift linkage and linkage in need of
lubrication. Hard shifting may also be caused by binding of the shift rails or forks.
Occasionally, hard shifting may be caused by a misaligned transmission case or a
problem in the clutch.
Hard shifting can be diagnosed easily. If the gearshift lever is hard to move even when
the engine is stopped, the shift linkage is probably the source of the problem. If the
gearshift lever moves easily when the engine is stopped but shifting becomes hard with
the engine running, the problem is probably in the vehicle clutch, or else the case is
misaligned.
In transmissions having an external shift linkage, hard shifting may be corrected by
adjusting or lubricating shift linkages. In contrast, if internal parts of a shift linkage are
bent or sticking, the transmission must be removed and disassembled to make repairs.
Bad synchronizers, which can be responsible for hard shifting, or clutch problems wil
require transmission removal. Misalignment problems may require transmission
8-6
NAVEDTRA
14050A