© National Instruments
|
2-11
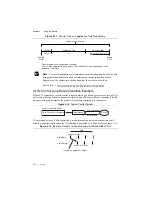
Passband
The signals within the passband have frequency-dependent gain or attenuation. The small
amount of variation in gain with respect to frequency is called the passband flatness. The digital
anti-alias filters of the NI PXIe-4302/4303 adjust the frequency range of the passband to match
the sample rate. Therefore, the amount of gain or attenuation at a given frequency depends on
the sample rate.
Stopband
The digital anti-alias filter significantly attenuates all signals above the stopband frequency to
prevent aliasing. Therefore, the stopband frequency scales precisely with the sample rate. The
stopband rejection is the minimum amount of attenuation applied by the anti-alias filter to all
signals with frequencies within the stopband.
Alias-Free Bandwidth
Any signal that appears in the alias-free bandwidth of the NI PXIe-4302/4303 is not an aliased
artifact of signals at a higher frequency. The alias-free bandwidth is defined by the ability of the
filter to reject frequencies above the stopband frequency, and it is equal to the sample rate minus
the stopband frequency.
Filter Group Delay
The anti-alias digital filtering performed by the NI PXIe-4302/4303 produces a delay of many
samples worth of time between when an event occurs on the input signal going into the
NI PXIe-4302/4303 and when the data associated with that event is available at the output of the
acquisition and filtering process. This delay is called the group delay.
In order to simplify the process of acquiring data from the NI PXIe-4302/4303 modules and
correlating that data with data from other modules, the NI PXIe-4302/4303 compensates for this
group delay in the following ways:
•
The Sample Clock output from the NI PXIe-4302/4303 is generated at the point in time
when the input signal is valid at the ADC input pins. When acquiring data, the
NI PXIe-4302/4303 generates a Sample Clock, then waits for the data associated with that
Sample Clock to be acquired, then returns that data. As a result, any other acquisitions
timed with this Sample Clock line up with the data returned by the NI PXIe-4302/4303.
•
Any triggers generated or received by the NI PXIe-4302/4303 are interpreted based on their
relationship to the Sample Clock being generated. For example, a Start Trigger that starts
an acquisition results in data from the next Sample Clock being returned as the first point
in the acquisition. Refer to the
section for more details about
how this affects analog trigger events.