13-18
DSP56367
MOTOROLA
Timer/ Event Counter
Timer Modes of Operation
These functions are available only on timer 0.
13.4.2.1
Measurement Accuracy
The external signal is synchronized with the internal clock used to increment the counter. This
synchronization process can cause the number of clocks measured for the selected signal
value to vary from the actual signal value by plus or minus one counter clock cycle.
13.4.2.2
Measurement Input Width (Mode 4)
In this mode, the timer 0 counts the number of clocks that occur between opposite edges of an
input signal.
Set the TE bit to clear the counter and enable the timer. Load the timer’s count value into the
TLR. After the first appropriate transition (as determined by the INV bit) occurs on the TIO0
input pin, the counter is loaded with the TLR value on the first timer clock signal received
either from the DSP56367 clock divided by two (CLK/2) or from the prescaler clock input.
Each subsequent clock signal increments the counter.
If the INV bit is set, the timer starts on the first high-to-low (1 to 0) signal transition on the
TIO0 signal. If the INV bit is cleared, the timer starts on the first low-to-high (0 to 1)
transition on the TIO0 signal.
When the first transition opposite in polarity to the INV bit setting occurs on the TIO0 signal,
the counter stops. The TCF bit in the TCSR is set and a compare interrupt is generated if the
TCIE bit is set. The value of the counter (which measures the width of the TIO0 pulse) is
loaded into the TCR. The TCR can be read to determine the external signal pulse width.
If the TRM bit is set, the counter is loaded with the TLR value on the first timer clock received
following the next valid transition occurring on the TIO0 input pin and the count is resumed.
If the TRM bit is cleared, the counter continues to be incremented on each timer clock.
This process is repeated until the timer is disabled (i.e., TE is cleared).
If the counter overflows, the TOF bit is set, and if TOIE is set, an overflow interrupt is
generated.
The counter contents can be read at any time by reading the TCR.
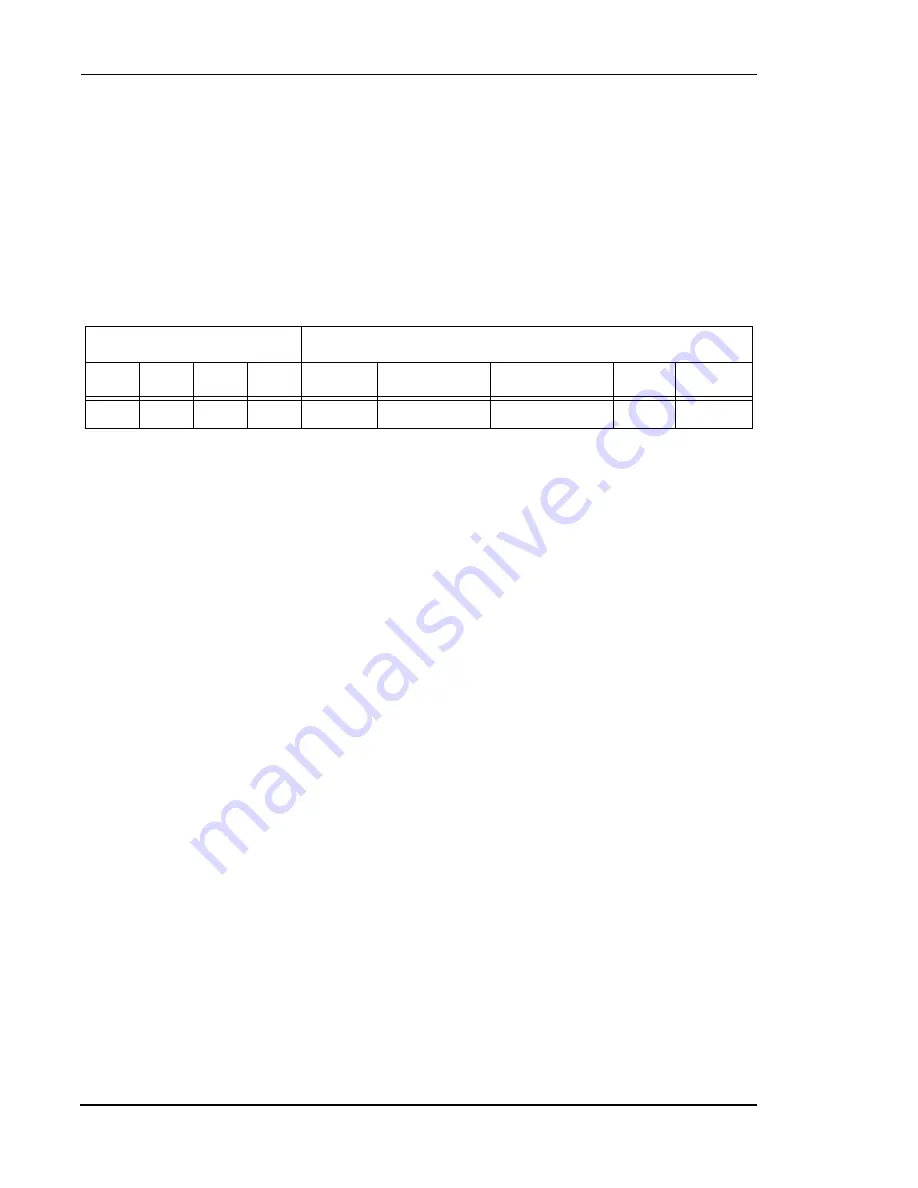
Bit Settings
Mode Characteristics
TC3
TC2
TC1
TC0
Mode
Name
Kind
TIO0
Clock
0
1
0
0
4
Input Width
Measurement
Input
Internal
Summary of Contents for DSP56367
Page 16: ...xvi MOTOROLA CONTENTS Paragraph Number Title Page Number ...
Page 22: ...xxii MOTOROLA List of Figures Figure Number Title Page Number ...
Page 26: ...xxvi MOTOROLA List of Tables Table Number Title Page Number ...
Page 148: ...4 6 DSP56367 MOTOROLA Design Considerations PLL Performance Issues ...
Page 248: ...9 30 DSP56367 MOTOROLA Serial Host Interface SHI Programming Considerations ...
Page 306: ...10 58 DSP56367 MOTOROLA Enhanced Serial Audio Interface ESAI ESAI Initialization Examples ...
Page 389: ...Bootstrap ROM Contents MOTOROLA DSP56367 A 15 end ...
Page 390: ...A 16 DSP56367 MOTOROLA Bootstrap ROM Contents ...
Page 432: ...C 8 DSP56367 MOTOROLA JTAG BSDL ...
Page 484: ...D 52 DSP56367 MOTOROLA Programmer s Reference ...
Page 490: ...E 6 DSP56367 MOTOROLA Power Consumption Benchmark ...
Page 516: ...F 26 DSP56367 MOTOROLA IBIS Model ...
Page 522: ...Index 6 MOTOROLA Index ...
Page 523: ......