MCAC-VTSM-2015-10
R410A All DC Inverter V5 X Series 50Hz
Installation 103
Outer Diameter
(mm)
Material
Minimum
Thickness
(mm)
Outer
Diameter
(mm)
Material
Minimum
Thickness
(mm)
Outer Diameter
(mm)
Material
Minimum
Thickness
(mm)
Ф6. 35
O
0. 8
Ф19. 1
O
1. 0
Ф38. 1
1/2H
1. 5
Ф9. 53
O
0. 8
Ф22. 2
1/2H
1. 2
Ф44.5
1/2H
1. 5
Ф12. 7
O
0. 8
Ф25. 4
1/2H
1. 2
Ф54. 0
1/2H
1. 8
Ф15. 9
O
1. 0
Ф28. 6
1/2H
1. 3
Ф67. 0
1/2H
1. 8
4.4.2
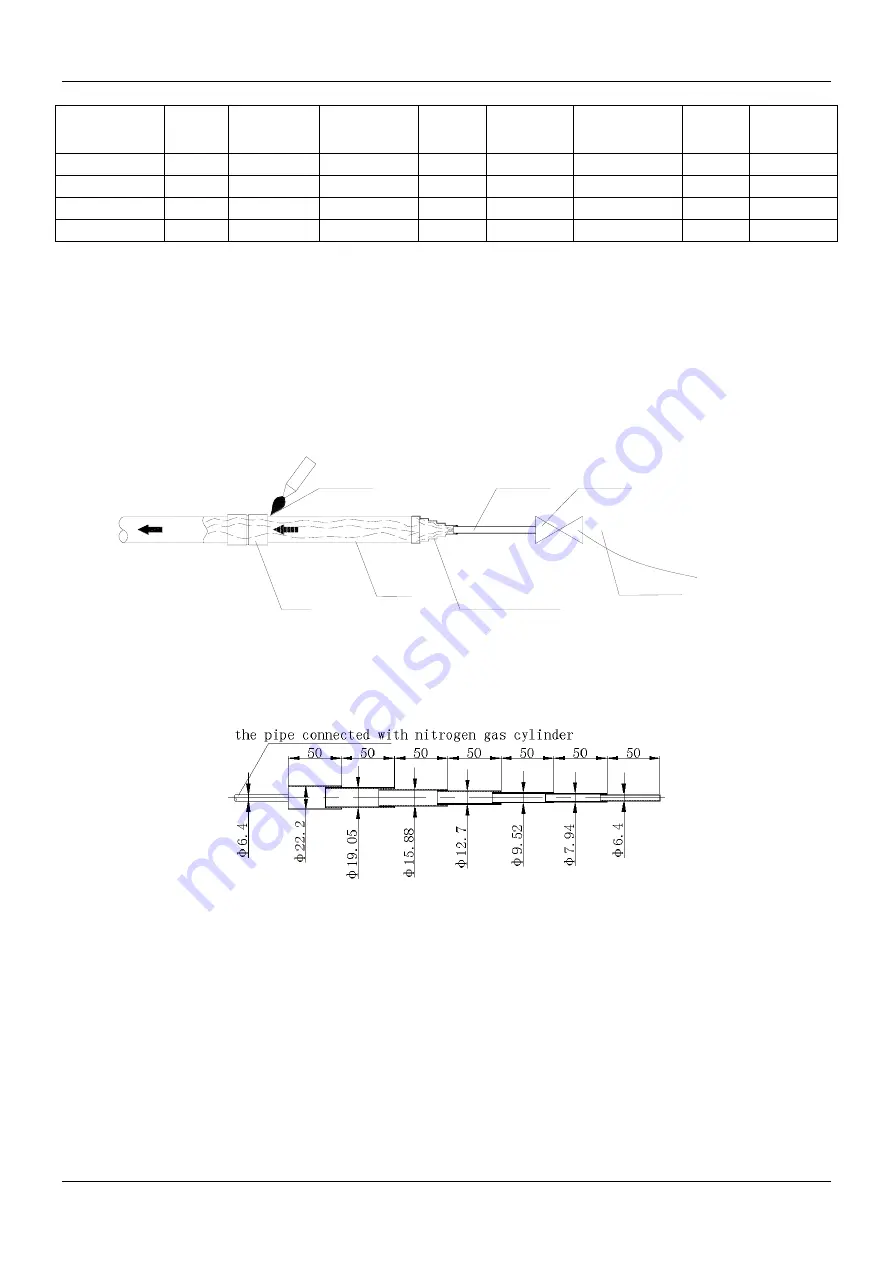
Nitrogen filling to protect copper pipe during brazing
1. Purpose: Avoid oxide scale formation on the inner wall of the copper pipe caused by high temperature
2. Risks of non-protective welding:
If insufficient nitrogen is charged during brazing, oxides will form on the inner wall of the copper pipe. These
oxides will block the refrigerant system, which will lead to various malfunctions such as compressor burnout,
poor cooling efficiency.
To avoid these problems, charge nitrogen continuously into the refrigerant pipe during brazing, and ensure that
the nitrogen continuously passes through the operating point until the welding is completed and the copper
pipe cools down completely. The diagram for nitrogen charging is shown below.
copper pipe 1/4"
copper pipe fittings
copper pipe
hign pressure flexible pipe
valve
nitrogen charging connecting fitting
brazing weld part
oxygen
nitrogen
3. Making nitrogen-charging pipe joint
When welding the pipe joint, connect the nitrogen-charging joint to the pipe fittings to be welded.
The nitrogen-charging joint is shown below:
4. Cautions for welding pipe fittings
1) Adopt transition pipe.
2) Charge nitrogen from the side of the short pipe, because short distance may result in perfectible nitrogen
replacement effect.
















































