Page 37
in motor vehicles should be used to reduce the risk of serious injuries to
wheelchair occupants
Alterations or substitutions should not be made to the wheelchair or seating
system structural members, or to its parts and components, without
consulting the wheelchair manufacturer
The use of postural pelvic belts attached to the wheelchair base or seat frame
is encouraged during travel, but these belts should be positioned so they
don’t interfere with the proper positioning of crashworthy belt restraints and
should not be relied on for occupant protection in crash situations unless the
postural belt has been designed to comply with, and perform to, requirements
of RESNA WC4, Section 19 and ISO 7176, Section 19
Both pelvic and shoulder belt restraints that comply with RESNA WC4,
Section 19 and ISO 7176, Section 19 should be used to limit occupant
movement in a crash and reduce the likelihood of injury
Belt restraints should be positioned on wheelchair occupants in accordance
with the wheelchair tie down and occupant restraint system and the
manufacturer’s instructions
Whenever possible, auxiliary wheelchair equipment should be removed from
the wheelchair and stored in a cargo area or secured in the vehicle during
transit, or effectively secured to the wheelchair so that it does not break loose
and cause injury to vehicle occupants in a crash
Rigid trays on wheelchairs that are not specifically designed for use during
travel in motor vehicles should be either removed and stored separately in the
vehicle or be secured to the wheelchair so it will not break free in a crash.
Additionally, the tray should be positioned with a gap of at least 75mm(3 in.)
between the tray and the wheelchair occupant’s abdomen and/or chest so as
not to interfere with proper belt restraint use and have energy absorbing
padding placed in the gap between the tray edge and the wheelchair occupant
The wheelchair manufacturer should be consulted for questions about using
the wheelchair for seating in a motor vehicle,
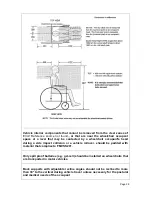
Sufficient forward and rearward clear space should be provided around the
wheelchair occupant as shown in Figure 14.
The forward clear space zone (FCZ) needs to be larger when a shoulder belt
restraint is not used