21
G-Link-200-OEM
USER MANUAL
5.4.3 Under-sampling
Under-sampling happens when there are not enough samples to accurately calculate a value
for a derived channel. The user should pick a window size that contains at least two periods of
the lowest rate input signal to be measured. The more information that can be included in the
derived calculation the more accurate the calculation.
For derived channels that use Fourier transforms on raw data, such as IPS, the chunk size will
limit the input frequency range rather than the window size. If the chunk size is at its maximum
size the only way to gain accuracy for lower frequencies is to reduce the sample rate.
5.4.4 Incoherence
Derived channels are most accurate when the window time is a multiple of the period of the
input signal, meaning that the window is coherent with the input signal. When the window is
not coherent with the input signal, the window will end up with a fraction of a period of the
input signal at the end, which will skew the derived calculation for the window in some cases.
Inaccurate derived values due to incoherence can be mitigated by using a larger window size.
The more input signal periods sampled within a window the more accurate the calculation.
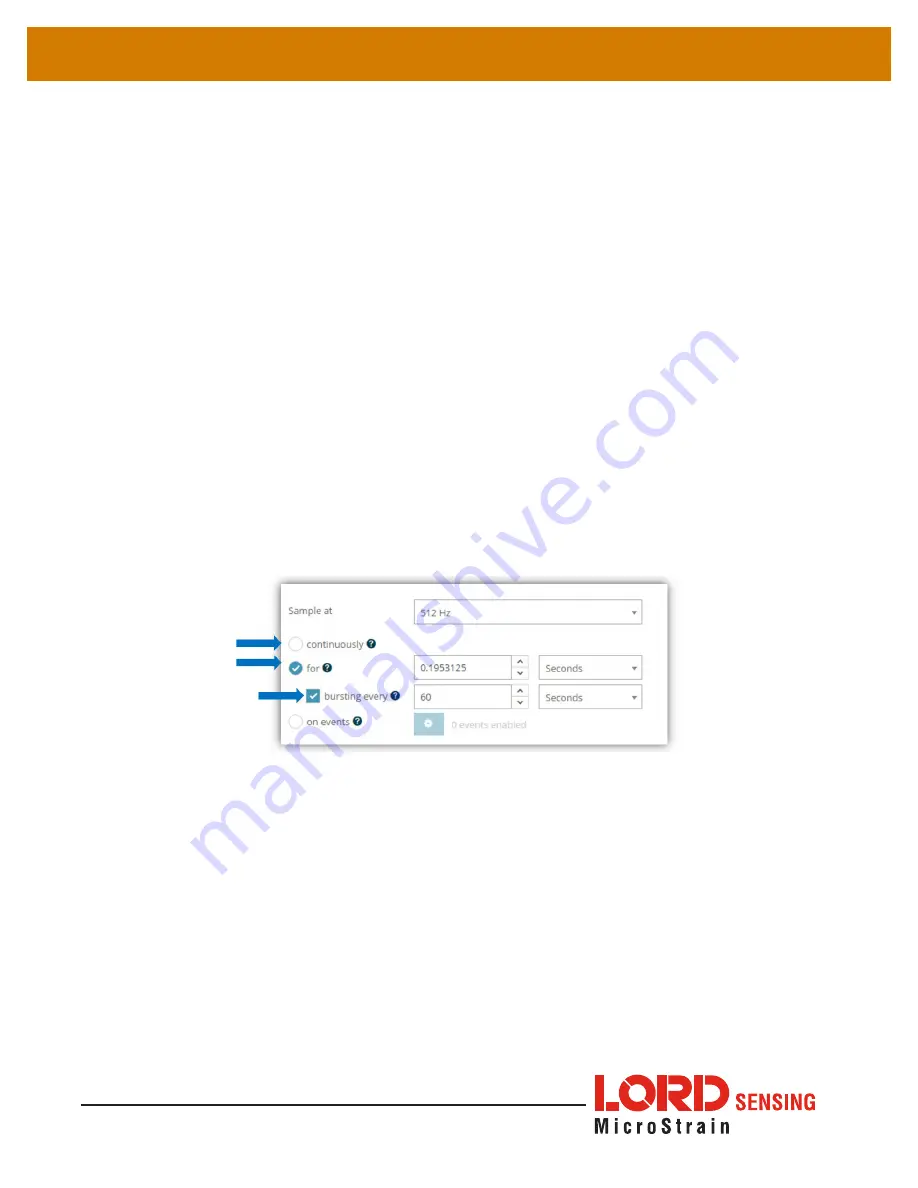
5.5 Sampling Operations Options
There are four sampling operations options for the G-Link-200-OEM, including Continuous,
Limited, Periodic Burst, and Event Triggered.
Figure 20. Sampling Operations Menu
















































