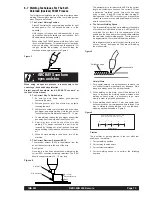
Refer to Figure 7.
1.
Learn to strike an arc by positioning the gun over the joint
and touching the wire to the work.
2.
Position face shield to protect face and eyes.
3.
Depress gun trigger, hold gun so contact tip to work
distance is about 10 to 12 mm and the gun is at proper angle.
4.
After you strike the arc, practice the correct electrical
stickout. Learn to distinguish it by its sound.
5.
When you are sure that you can hold the correct electrical
stickout, with a smooth “crackling” arc start moving. Look at
the molten puddle constantly, and look at the “ridge” where
the metal solidifies.
6.
Run beads on a flat plate. Run them parallel to the top edge
(the edge farthest away from you). This gives you practice
in running straight welds, and also gives you an easy way
to check your progress. The 10th weld will look
considerably better than the first weld. By constantly
checking on your mistakes and your progress, welding will
soon be a matter of routine.
5.8 Machine Set Up for the GMAW (MIG)
Process and Gas Shielded GCAW
Processes
1.
The REDI-MIG 455 Remote comes ready for welding using
the MIG process.
2.
See the Procedure Welding Guide on the inside of wire
feed section door for information on setting the controls.
3.
Set the “Voltage” and “Wire Speed” controls to the settings
suggested on the Procedure Welding Guide for the welding
wire and base metal thickness being used. ’
4.
Check that the polarity is correct for the welding wire being
used. Set the polarity for DC(+) when welding with the
GMAW (MIG) process. See Section 1.5 for instructions for
changing polarity.
5.
Check that the gas nozzle and proper size liner and contact
tip are being used and that the gas supply is turned on. Set
for 7 to 10 L/min. under normal conditions, increase to as
high as 17 L/min. under drafty (slightly windy) conditions.
6.
Connect work clamp to metal to be welded. Work clamp
must make good electrical contact to the work piece. The
work piece must also be grounded as stated in the “Arc
Welding Safety Precautions” at the beginning of this
manual.
5.9 Welding Techniques for the GMAW (MIG)
Process
Four simple manipulations are of prime importance when
welding. With complete mastery of the four, welding will be
easy. They are as follows:
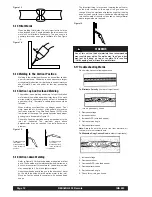
1. The Correct Welding Position
Figure 8 illustrates the correct welding position for right
handed people. (For left handed people, it is the
opposite.)
When GMAW (MIG) welding on sheet metal, it is
important to use the “forehand” push technique.
Hold the gun (of the gun and cable assembly) in your
right hand and hold the shield with your left hand. (Left
handers simply do the opposite.) Weld from right to left
(if you are right handed). This results in a colder weld
and has less tendency for burn through.
When using an open arc process, it Is necessary to use
correct eye, head and body protection.
Protect yourself and others, read “ARC RAYS can burn” at
the front of this manual.
2. The Correct Way To Strike An Arc
1. Be sure the work clamp makes good electrical
contact to the work.
2. Position gun over joint. End of wire may be lightly
touching the work.
3. Position face shield to protect face and eyes, close
gun trigger, and begin welding. Hold the gun so that
the contact tip to work distance is about 10 - 12 mm.
4. To stop welding, release the gun trigger and pull the
gun away from the work after the arc goes out.
5. A ball may form at the tip end of the wire after
welding. For easier restrikes, the ball may be
removed by feeding out a few inches of wire and
cutting off the end of the wire with wire cutters.
6. When no more welding is to be done, close the valve
on the gas cylinder, momentarily operate the gun
trigger to release gas pressure, then turn off the
machine.
Figure 7
Mild Steel Plate
3.0mm
Electrode
1.2mm
Innershield 211 MP
Voltage Setting
Af
Wire Feed Speed
4
For the REDI-MIG 455 Remote, use the following:
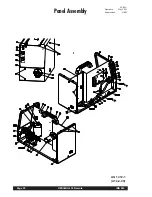
Figure 8
ARC RAYS can burn
eyes and skin
Figure 9
Page 16
REDI-MIG 455 Remote
IMA 603