3. TECHNICAL BRIEF
- 27 -
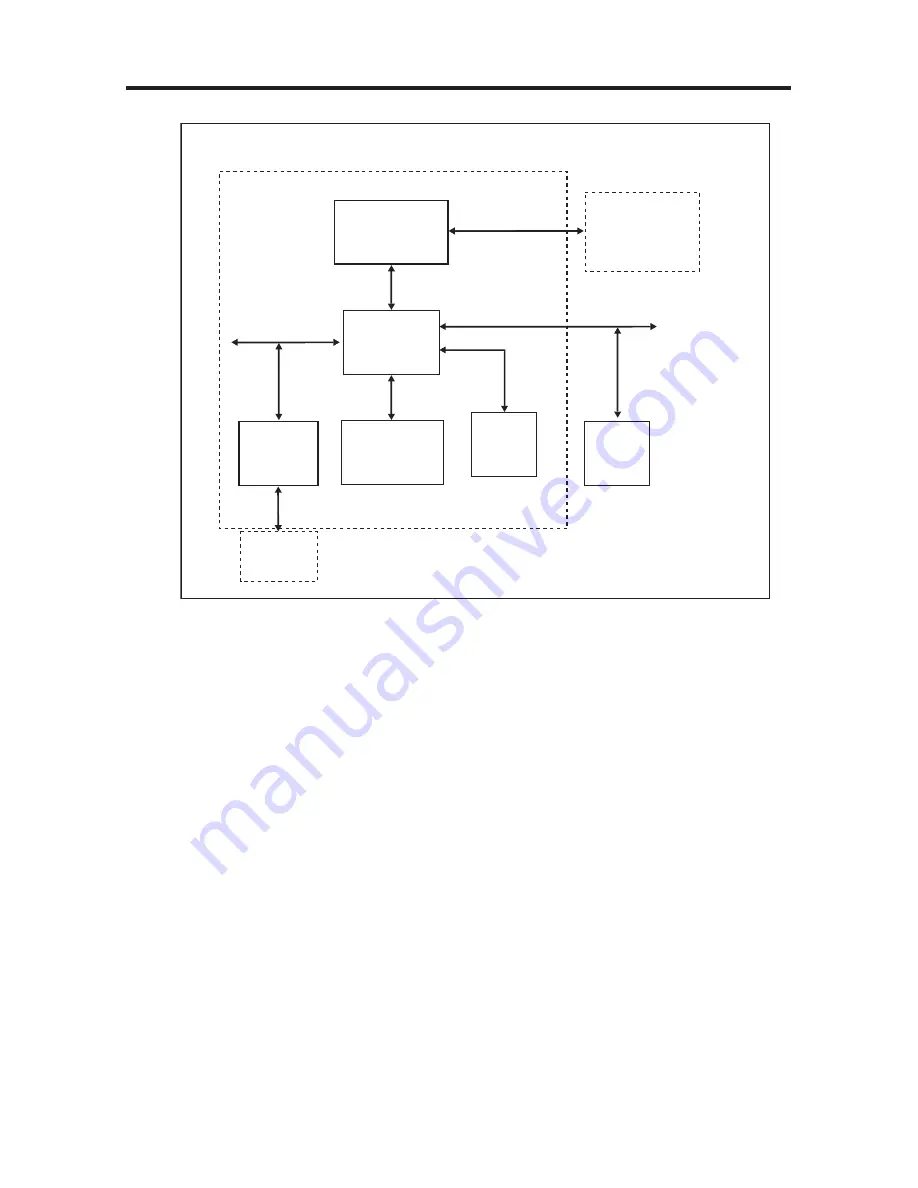
Figure 3-10 AD6527 ARCHITECTURE
AD6527/AD6527B
AD6535
Audio Baseband
and Power
Management
DSP
SRAM
FLASH
MMI
USC
Peripheral
RF-Control
Subsystem
Subsystem
Subsystem
(ARM7TDMI
®
)
DMA and BUS
ARBITRATION
Serial Link
DSP BUS
RBUS IM
EBUS
PBUS
SBUS
MUC
The internal architecture of AD6527 is shown above Figure 3-10. AD6527 regroups three main subsys-
tems connected together through a dynamic and flexible communication bus network. It alsoincludes
onboard system RAM (SRAM) and interfaces with external Flash Memory, Basebandconverter functions,
and terminal functions like MMI, SIM and Universal System Connector (USC).The Digital Signal
Processing (DSP) subsystem primarily hosts all the speech processing, channel equalization and channel
codec functions. The code used to implement such functions can be storedin external Flash Memory and
dynamically downloaded on demand into the DSP’sprogram RAM andInstruction Cache.
The micro-controller subsystem supports all the GSM terminal software, including the layer 1, 2 and 3of
the GSM protocol stack, the MMI, and applications software such as data services, test and mainte-
nance. It is tightly associated with on-chip system SRAM and also includes boot ROM memory with a
small dedicated routine to facilitate the initialization of the external Flash Memory via code download
using the on-chip serial interface to the external Flash Memory interface.The peripheral subsystem is
composed of system peripherals such as interrupt controller, real timeclock, watch dog timer, power man-
agement and a timing and control module. It also includes peripheral interfaces to the terminal functions:
keyboard, battery supervision, radio and display. Boththe DSP and the MCU can access the peripheral
subsystem via the peripheral bus (PBUS).For program and data storage, both the MCU subsystem and
the DSPsubsystem can access the onchip system SRAM and external memory such Flash Memory. The
access to the SRAM module ismade through the RAM Bus (RBUS) under the control of the bus arbitra-
tion logic. Similarly, access tothe Flash Memory is through the parallel External Bus (EBUS).
Summary of Contents for B2050
Page 7: ... 6 2 PERFORMANCE 2 PERFORMANCE 2 1 H W Features ...
Page 8: ... 7 2 PERFORMANCE ...
Page 9: ... 8 2 PERFORMANCE 2 2 Technical Specification ...
Page 10: ... 9 2 PERFORMANCE ...
Page 11: ... 10 2 PERFORMANCE ...
Page 12: ... 11 2 PERFORMANCE ...
Page 13: ... 12 2 PERFORMANCE ...
Page 57: ... 56 3 Checking Ant SW Mobile SW 4 TROUBLE SHOOTING ...
Page 67: ... 66 TEST POINT 4 6 LCD Trouble 4 TROUBLE SHOOTING ...
Page 70: ... 69 4 TROUBLE SHOOTING TEST POINT 4 7 Speaker Trouble ...
Page 77: ... 76 4 TROUBLE SHOOTING 4 10 KEY backlight Trouble TEST POINT ...
Page 92: ...5 DOWNLOAD AND CALIBRATION 91 5 2 Calibration ...
Page 93: ... 92 5 DOWNLOAD AND CALIBRATION ...
Page 97: ......
Page 103: ... 102 Figure 8 1 B2050 BOTTOM SIDE PCB LAYOUT 8 PCB LAYOUT ...
Page 104: ... 103 8 PCB LAYOUT Figure 8 1 B2050 TOP SIDE PCB LAYOUT ...
Page 105: ......
Page 113: ...10 STAND ALONE TEST 112 ...
Page 117: ......
Page 119: ......
Page 132: ... 131 ...
Page 133: ... 132 ...
















































