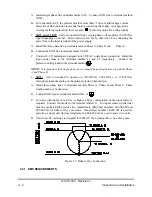
3.7 SERIES OPERATION MASTER/SLAVE
This configuration allows the customer to use two or more power supplies as a single unit.
The master power supply controls the output voltage across the load. The supply that is
designated the master should be set to a voltage higher than or equal to that of the slave. The
voltage of the slave is determined by R
X
.
, V
S
≤
V
M
R
X
=
(
V
M
+
V
S
)
V
SMAX
.
V
S
−
5
K
W
V
M
, output voltage of master power supply.
V
S
, desired output voltage of slave power supply.
V
SMAX
, maximum rated output voltage of slave power supply.
1. Turn circuit breaker off.
2. Connect load as shown in Figure 3.13.
3. Disconnect link between TB1/J1-3 and TB1/J1-4 on slave.
4. Connect R
X
between TB1/J1-4 of slave and TB1/J1-2 of master. Refer to Figure 3.13.
5. Rotate voltage control of slave fully clockwise.
6. Turn on slave(s) and then master.
7. Adjust master supply for desired output voltage across load.
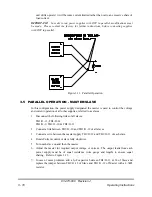
Figure 3.14: Series Operation, Master/Slave
3.8 REMOTE METERS (P.S. WITH OUTPUT OF 300V OR LESS)
A remote voltmeter may be connected between TB1/J1-2 (positive) and TB1/J1-7 (negative).
If remote sensing is also being used, the remote voltmeter will indicate the voltage at the load.
To indicate the voltage at the power supply output terminals, connect the remote voltmeter
between terminals TB1/J1-1 (positive) and TB1/J1-8 (negative).
A remote millivoltmeter, may be connected between terminals TB1/J1-12 (negative) and
TB1/J1-13 (positive). A voltage of 0 to 100mV across these terminals indicates output
current from zero to full rating, unless otherwise specified (see main schematic). To
compensate for voltage drops in long remote ammeter leads, a meter movement having a full
scale sensitivity of less than 100mV is used in series with a calibrating resistor.
83-473-000 Revision J
3 - 12
Operating Instructions