2: General Description
10
TS_619_00 PW9000DPA S2 User Manual 13/3/17
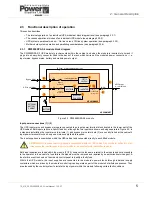
2.3.4 Parallel system operation
All the modules fitted in a UPS cabinet inherently operate as a parallel system as their outputs are connected in parallel at
the cabinet’s output terminals. The electronic control system built into each module ensures that:
• The modules are always frequency-synchronised to each other – and to the bypass mains (when present).
• The modules equally share the load current.
• The modules’ load transfer operation is synchronised such they ALL transfer their output between inverter and
bypass simultaneously when commanded from any one module.
The PW9000DPA S2 UPS system can be expanded by connecting up to six PW9000DPA S2 UPS cabinets in parallel;
and when two or more cabinets are connected in this way, all the UPS modules within them are effectively paralleled
together. For example: a maximum system capacity is obtained by connecting together six DPA-250 cabinets, each fully
populated with DPA-50 modules, which results in a total of thirty (50kVA) modules operating in parallel to provide a system
capacity of 1500kVA.
System expansion
Some UPS applications present a low initial power requirement which increases over time as the application grows; and it
is therefore essential that the installed UPS system can be expanded to meet the growing demand without compromising
the existing load. This requirement is well met with the ‘hot swappable’ feature of the PW9000DPA S2 UPS modules,
whereby an additional module can be inserted into a vacant slot in an existing cabinet without disturbing the load.
Note: If the expansion requires an additional cabinet the system will have to be shut down while the cabinet is installed.
‘Capacity’ versus ‘redundant module’ system
A parallel UPS system can be operated as either a ‘capacity’ or ‘redundant’ module system.
A ‘capacity’ system is rated such that ALL the UPS modules are required to furnish the specified full load power and the
loss of one module will automatically transfer the load to the bypass supply.
In a ‘redundant-module’ system, the system contains at least one UPS module over and above that required to supply the
full load and it is possible to lose a module without transferring the load to the bypass supply or in any way disrupt the UPS
output. A system operating with a redundant module is inherently the most reliable.
A parallel system operating with one redundant module is known as an ‘N+1’ system.
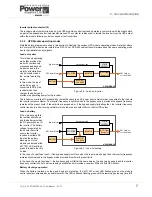
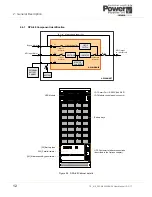
Parallel control bus
All the UPS modules within a cabinet, and between cabinets, are connected to a parallel control bus which carries several
control signals used for frequency synchronisation, load sharing etc. Each UPS module can electronically compare its own
frequency and output current with that of its neighbouring module and make any necessary fine adjustments to its control
logic to achieve balanced conditions across the system.
The parallel control logic observes one UPS module as being the ‘master’ and the others as ‘slaves’. However if the
‘master’ module goes faulty at any time the next module in the chain (a former ‘slave’) will immediately take over the role
of ‘master’ and the former ‘master’ module will turn off. The ‘master/slave’ configuration is set during commissioning.
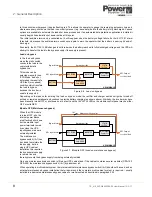
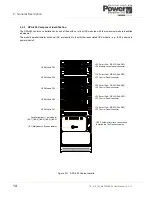
During commissioning, the UPS modules are also assigned a numerical ID according to their position in the cabinet, with
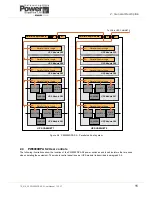
the bottom module being given the lowest number. Figure 2.8 shows two DPA-250 cabinets with the modules in cabinet 1
assigned an ID of ‘P01’ to ‘P05’ and those in cabinet 2 an ID of ‘P06’ to ‘P10’ (‘P’ indicates that the modules are part of a
Parallel system). The module ID is used by the control and monitoring logic.
Key Point:
When planning a multi-cabinet system, it is not necessary to fully populate one cabinet with UPS
modules before installing the next cabinet. For example, if it is known at the outset that a 200kVA initial load
requirement is likely to increase to 400kVA, it makes sense to install and cable-up two DPA-250 cabinets and
distribute the initial requirement of four UPS modules between them.