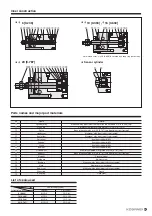
5
Installation and adjustment
Always read these precautions carefully before use.
WARNING
WARNING
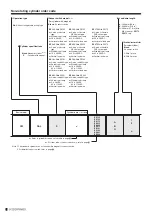
1. Check for internal voltage drop of sensor switches.
When reed sensor switches with indicator lamps or 2-lead
wire solid state sensor switches are connected in series
causes increasing internal voltage drop, and the load may fail
to activate. Connecting n-pieces will drop the internal voltage
by n times as large.
Ensure the circuit satisfy the following inequality.
Power supply voltage — Internal voltage drop×n > Minimum
operating voltage of the load
In relays with rated voltage of less than 24VDC, check to see
the above inequality is satisfied even when n
=
1.
When the above inequality is not satisfied, select a reed sen-
sor switch without indicator lamp.
2. Do not use Koganei sensor switches with other com-
pany's cylinders.
The sensor switches are designed for use with our Koganei
cylinders only. Using with other company's cylinders may not
function properly.
1. Check the specifications.
Using outside of specification range in voltage, current, temper-
ature, shock, etc. creates the risk of breakdown or malfunctions
of the product. Read the specification carefully before using.
2. Avoid mounting cylinders in close proximity to each other
When more than two cylinders with sensor switches are used
close to each other, see page
E
. This can cause the sensor
switch to malfunction due to the magnetic interference with
each other.
3. Where the position detection is made at mid-stroke,
be cautious against the sensor switch ON time.
Be aware that, when the sensor switch is mounted at interme-
diate point of cylinder stroke to detect passing of the piston,
too fast speed of the piston can shorten the sensor switch
operation time, causing the load, such as programmable con-
trollers, to fail to operate.
The highest detectable cylinder speed is
4. Keep wiring as short as possible.
The wiring for solid state sensor switches must be 30 m
[98.4ft] or shorter, as stipulated by EN standard. For reed sen-
sor switches, the longer wiring (10 m [32.8 ft] or longer) will
lead to the larger capacitive surge current, which reduces the
operating life of sensor switches. When a longer wiring cannot
be avoided, provide the protective circuit described in the cat-
alog.
If the load is inductive or capacitive, provide the appropriate
protective circuit as described in the catalog.
5. Avoid repeated bending or excessive pulling of lead
wires.
Applying repeated bending or pulling force on the lead wires
could cause breaking the wire.
6. Check for leakage current.
2-lead wire solid state sensor switches produce the current
(leakage current) even at off condition to activate the internal
circuit. Ensure that they satisfy the following inequality:
Input off current of programmable controller > Leakage current
If above inequality is not satisfied, select 3-lead wire solid
state sensor switch. And, if n-pieces sensors are connected in
parallel, the leakage current increases by n times.
1. Do not apply an external magnetic field to the sensor
switch while the cylinder is in operation.
This may cause unintended operation, thereby damaging the
device and causing personal injury.
V [mm/s] =
Sensor switch operating range [mm]
Time required for load operation [ms]
×1000
Design and Selection
CAUTION
1. Ensure a safe installation environment for the cylin-
ders with sensors.
The sensor switch should not be used in a location where
large current or high magnetic field is present. It could result
in erratic operation.
Do not use magnetic material for the mounting portion. This
may cause erratic operation.
2. Install the sensor switches in the center of their
operating range.
Adjust the mounting position of the sensor switch so that the
piston can stop in the center of the operating range (the sen-
sor turned-on range). Setting the switch ON the end of the
operating range (at the boundary of ON/OFF) may cause the
operation to be unstable. Also be aware that the operating
range will vary according to the temperature change.
3. Follow the tightening torque for the sensor switches
when mounting.
Tightening the screw exceeding the allowable tightening
torque may damage the mounting thread, mounting bracket,
sensor switch etc. In addition insufficient tightening torque
could cause the sensor switch position to be changed, there-
by resulting in unstable operation. For details about tightening
torque, refer to Page
E
.
4. Do not carry the cylinder by its mounted sensor
switch's lead wire.
After mounting a sensor switch on the cylinder, do not carry
the cylinder by grabbing the lead wire. This may not only dam-
age the lead wire but also apply stress to the inside of the
sensor switch that may damage internal elements, so never
perform such behavior.
5. Do not drop the sensor switches or bump them
against other objects.
When handling the product, take care to avoid dropping it,
allowing it to bump against other objects, or otherwise sub-
jecting it to excessive impact (294.2 m/s [30G] or more).
In the case of reed sensor switches, such behavior may
cause the contact to malfunction, thereby giving a signal
instantaneously or turning off the signal. And, this may
change the contact interval, thereby deteriorating the sensor
switch's sensitivity. As such, this may cause the device to mal-
function. Even if the sensor switch case is not damaged, the
inside of the sensor switch may be damaged, causing erratic
operation.
CAUTION
Safety Precautions (Sensor switch)
Summary of Contents for YMDA Series
Page 34: ...33 MEMO ...