-10-
-11-
General welding information
2
1
4
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
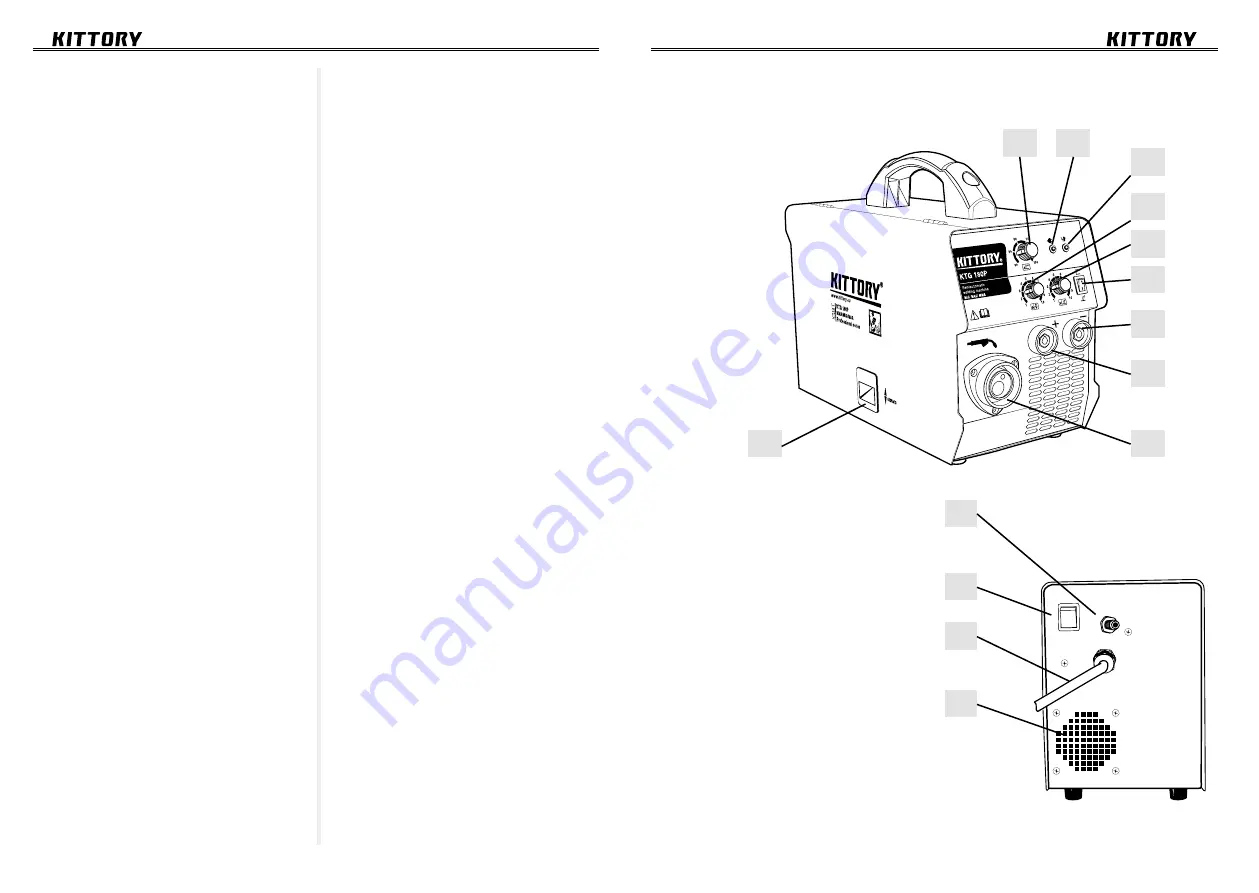
Physical configuration and controls of KTG 160P, KTG 180P, KTG 200P
11.
Gas cylinder connector.
12.
Power switch button.
13.
Power supply cord.
The power-supply cord is designed
for power connection of the welding
machine to an electric power network
rated at 150-230Volts, 50Hertz. For
reliable power supply of the welding
machine, an outlet with a grounding
contact and a circuit breaker with a cur-
rent rating of at least 50A are required.
14.
Cooling fan grid
General welding information
General welding
information
Semiautomatic welding machine is
designed for manual inert-gas arc weld-
ing. The shielding gas or gas mixture
may consist of the following: carbon
dioxide, argon or their mixture.
The welding machine has a metal
case with an opening wall. On the
front panel there is the welding current
selector, the wire feed speed control,
the power indicator, alarm indicator. The
machine is equipped with a forced venti-
lation system, therefore, it is strictly for-
bidden to cover any ventilation openings
in the metal case.
The principle of semiautomatic
welding machine. The machine converts
an AC voltage of 50Hz into a 400V DC
voltage that is converted to a high-fre-
quency modulated voltage and rectified.
Welding is carried out by a melted elec-
trode in a shielding gas environment.
The electrode is a metal wire fed by feed
rolls into the weld pool.
The shielding gas is fed to the
welding pool from the attached cylinder
through the solenoid valve. The machine
has built-in protection against overheat-
ing and is equipped with current adjust-
ment conrol and wire feeder control,
depending on the material and the thick-
ness of the workpiece to be welded.
Component overview
1.
MMA welding current. Welding
current is selected depending on the
electrode diameter and thickness of the
workpiece.
2.
Power indicator. Indicates that the
welding machine is connected to the
electrical power supply.
3.
Alarm indicator. If the alarm indi-
cator light is on, the machine is over-
heated. When the breaker has tripped,
the power flowing to the electrical
circuit is interrupted, but the cooling
fan keeps working. After the operating
temperature has been restored, the cur-
rent supply to the output of the welding
machine is automatically switched on.
4.
MIG wire feed speed control
The welding current depends on the
feed rate of the electrode wire. The wire
feed speed prevents excessive weld
spatter, wire sticking to the workpiece or
arc breaking.
The wire feed speed is selected
experimentally and depends on the
wire diameter, the thickness of the
weld metal and the qualification of the
welder.
When welding current increases,
weld penetration increases too, it leads
to an increase in the proportion of the
base metal in the seam. The width of
the seam increases slightly at first, and
then decreases.
5.
Arc voltage regulator
When arc voltage increases, weld
penetration decreases and the width of
the seam increases. Excessive increase
in arc voltage leads to increased spat-
tering of melted metal, deterioration of
the gas shield and formation of pores in
the weld metal.
The arc voltage is set depending on
the selected welding current amperage.
6.
MIG/MMA switch.
7.
(–) “Mass” or negative welding
cable socket 10-25 mm
2
.
8.
(+) Positive welding cable socket
10-25 mm
2
.
9.
MIG torch line cable inlet.
10.
Wire feeder door lock.





























