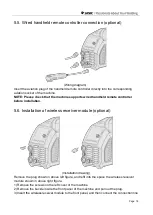
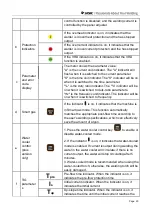
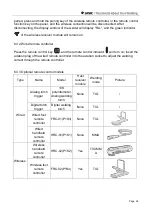
Page 32
lighting.
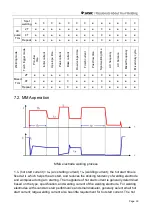
● Up-slope time (t2): Refers to the time as the current slowly rises from the initial current to
the peak current, which can be determined according to the usage and process
requirements.
● Peak current (I3): Set by the user according to the actual process requirements.
● Down-slope time (t4): Down-slope time refers to the time when the current drops from the
peak to the finish current, which can be determined according to the usage and process
requirements.
● Finish current (I5): In 4T operation mode, the arc is not extinguished after the current
down-slope and remains in a state of continuous arcing, which can avoid weld defects or
large craters caused by immediately cutting off the output. The operating current in this state
is called the finish current, which should be determined according to the process
requirements.
● Pre-flow time (t0): Refers to the time from pressing the torch trigger to sending argon gas to
arc starting. Generally, it should be greater than 0.5s to ensure that the gas has been sent to
the welding torch at normal flow when discharging arc initiation. It should be increased when
the gas pipe is long.
● Post-flow time (t6): Refers to time from cutting off the welding current to turning off gas the
valve in the welder. It should be determined according to the usage conditions and process
requirements; too long will cause waste of argon gas, but too short will cause oxidation of the
weld. The time shall be longer for AC TIG and special material welding.
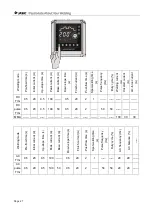
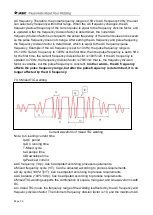
7.3.2 DC pulse TIG
DC pulse TIG welding current waveform
I1-Initial current
t0-Pre-flow time
I2-Current corresponding to the up-slope time
t1-Initial current period
I3-Set pulse current
t2-Up-slope time
I4-Current corresponding to down-slope time
t3-Peak current running period
I5-Finish current
t4-Down-slope time
IP-Pulse peak current
t5-Finish current period
Ib-Pulse base current
t6-Post-flow time
tb-Pulse base time