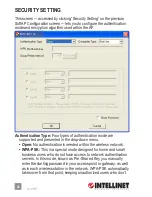
• WEP:
Enables the WEP Data Encryption. When the item is selected,
you need to continue setting the WEP Encryption keys.
• TKIP:
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol changes the temporal key
every 10,000 packets (a kind of message transmitted over a network.)
This ensures much greater security than the standard WEP security.
• AES:
AES has been developed to ensure the highest degree of
security and authenticity for digital information. It’s the most advanced
solution defined by IEEE 802.11i for security in the wireless network.
NOTE:
All devices in the network should use the same encryption
method to ensure the security of communications.
WPA Pre-Shared Key:
The WPA-PSK key can be 8 to 64 characters in
length and can be letters or numbers. This same key must be used on
all the wireless stations in the network.
WEP Key (Key#1–4):
WEP keys are used to encrypt data transmitted
in the wireless network. There are two types of key length: 64-bit and
128-bit. Assign a default encryption key (Key#1 to Key#4) by clicking
on the corresponding radio button. To fill in each text field:
• 64-bit:
Input 10-digit hex values (in the A-F, a-f and 0-9 range) or
5-digit ASCII characters (a-z and 0-9) as the encryption keys.
For example: “0123456aef“ or “test1.”
• 128-bit:
Input 26-digit hex values (in the A-F, a-f and 0-9 range) or
13-digit ASCII characters (“a-z” and “0-9”) as the encryption keys.
For example: “01234567890123456789abcdef“ or “administrator.”
The IEEE 802.1X specification describes a protocol that can be used for
authenticating both clients (802.1x Setting/Certification below) and servers
(802.1x Setting/CA Server below) on a network. The authentication
algorithms and methods are those provided by the Extensible Authentication
Protocol (EAP), a method of authentication that has been in use for a
number of years on networks that provide Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
support (as many Internet service providers and enterprises do). EAP
runs before network layer protocols transmit data over the link.
When an AP acting as an authenticator detects a wireless station on the
LAN, it sends an EAP request for the user’s identity to the device. In
turn, the device responds with its identity, and the AP relays this identity
to an authentication server (typically an external RADIUS server).
CONFIGURATION
15