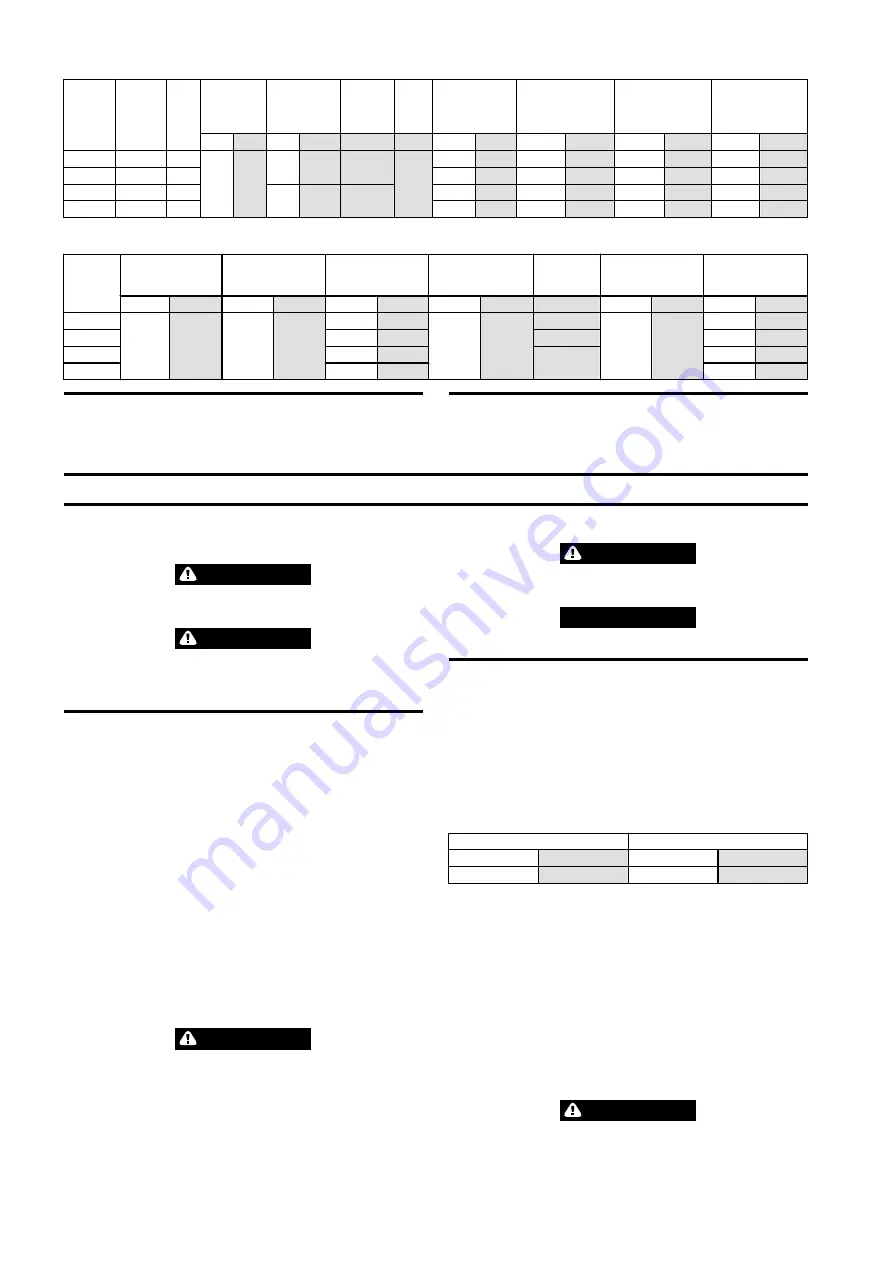
Table 2: Specifications
Hoist
Model
Rated
Capacity
metric
tons
Load
Chain
Falls
Flow
Recommended
Pressure @
Rated Load
Nominal
Hoist
Working
Pressure
Chain
Load
Size
Weight of Chain
per meter of lift
Unit Net Weight with
Standard 10 ft (3 m)
Lift
Minimum
Headroom
Maximum
Lifting
Speed
GPM L/min PSI
bar
bar
mm
lb
kg
lb
kg
in
mm
ft/min
m/min
LC2H060S
6
1
12.7
48
2,466
170
125
16 x 45
12.5
5.7
275
125
28.2
717
18.4
3.7
LC2H120D
12
2
25.1
11.4
375
170
37.2
945
9.2
1.9
LC2H180T
18
3
2,538
175
145
37.6
17.1
610
277
41.9
1,063
6.1
1.25
LC2H250Q
25
4
50.7
23.0
713
325
45.5
1,156
4.6
0.95
Table 3: Trolley Specifications
Hoist
Model
Flow
Travelling
Speed
Minimum
Headroom
Motor Trolley
Hydraulic Pressure
Min/Max
Trolley Flange
Adjustment
Minimum Curve
Radius
Total Weight With
Standard Lift
GPM
L/min
ft/min
m/min
in
mm
PSI
bar
mm
ft
m
lb
kg
LC2H060S
2.6
10
39
12
28.78
731
2,538
175
100–310
10
3
550
250
LC2H120D
39.17
995
130–310
738
335
LC2H180T
47.05
1195
160–310
1437
652
LC2H250Q
48.82
1240
1543
700
n
Capacity Information
LC2H
hoists are designed for lifting with a 5 to 1 minimum safety factor at rated
load.
n
Traceability
Load bearing parts are documented to provide traceability. Documentation includes
chemical and physical properties of raw material, heat treating, and hardening,
tensile and charpy tests as required for the part. Contact factory for documentation.
INSTALLATION
Prior to installing the product, carefully inspect it for possible shipping damage.
Products are supplied fully lubricated from the factory. Check oil levels and adjust as
necessary before operating product. Refer to “LUBRICATION” section on page 7
for recommended oils and lubrication intervals.
WARNING
• Prior to installation refer to Product Safety Information Manual for all
sections of Manual.
CAUTION
• Owners and users are advised to examine specific, local or other regulations,
including American National Standards Institute and/or OSHA Regulations
which may apply to a particular type of use of this product before installing
or putting product to use.
n
Mounting
Make certain your hoist is properly installed. A little extra time and effort in doing
so can contribute a lot toward preventing accidents and helping you get the best
service possible.
Always make certain the supporting member from which hoist is suspended is strong
enough to support weight of hoist, plus weight of maximum rated load, plus a
generous factor of at least 500% of the combined weights.
If hoist is suspended by a top hook, the supporting member should rest completely
within the saddle of the hook and be centered directly above hook shank. Do not use
a supporting member that tilts hoist.
n
Hook Mounted Hoist
Place hook over mounting structure. Make sure hook latch is engaged.
n
Trolley Mounted Hoist
When installing a trolley on a beam, measure beam flange and temporarily install
trolley on the hoist to determine exact distribution and arrangement of spacers.
Adjust spacers in accordance with trolley manufacturer’s literature to provide correct
distance between the wheel flange and beam. The number of spacers between trolley
side plate and mounting lug on the hoist must be the same on both sides in order to
keep hoist centered under I-beam. Remaining spacers must be equally distributed on
the outside of the side plates.
WARNING
• At least one mounting spacer must be used between the head of each trolley
bracket bolt and the trolley bracket and between each trolley bolt nut and
the trolley bracket. Failure to do this could cause hoist to fall when used
improperly.
Ensure trolley hanger capscrews or nuts are torqued in accordance with manufacturer’s
specifications. For installation of hoist and trolley on beam, make certain the side
plates are parallel and vertical.
After installation ensure beam stops are in place, operate trolley over entire length
of beam with a capacity load suspended 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cms) off the floor.
CAUTION
• To avoid an unbalanced load which may damage the trolley, the hoist must
be centered under the trolley.
NOTICE
• Trolley wheels ride on the top of the lower flange of the beam.
n
Hydraulic System
Refer to Dwg. MHP3136 on page 9.
n
Hoses
In order to maintain maximum efficiency of product, select size of hydraulic lines
according to maximum volume of oil to be used. If hydraulic lines used are too small,
they may cause excessive back pressure, generating heat and causing inefficiency
within the hydraulic system. Sizes in Table 4 ‘Hose Recommendations’ on page 4,
are to be used as a guide only. If trouble is experienced due to the use of long hoses,
it may be necessary to use hoses which are one size larger.
Table 4: Hose Recommendations
Oil Flow @ 3000 PSI max.
Pressure Hoses (inside diameter)
GPM
L/min
inch
mm
12.7
48
n
Fluid
The most frequent cause of malfunction or failure of hydraulic equipment is presence
of contaminants in hydraulic fluid. Reduce contaminants by using clean hydraulic
fluid, and changing the fluid before it deteriorates. When hydraulic fluid is changed,
also clean out the hydraulic reservoir. At a minimum, the required oil cleanliness level
is ISO 18/13 or better. Periodic checks which may be performed by the operator to
test hydraulic fluid cleanliness include:
1. Check for a major change in color or noticeable thickening, which are signs of
severe deterioration and indicate the need to change the fluid.
2. Check oil for foaming and aeration which may indicate low oil level in hydraulic
tank, leaks, faulty hydraulic line connections or moisture build-up in oil.
ISO VG 30, 46 and 68 oils will give good results under normal temperature conditions.
The use of an oil having a high viscosity index will minimize cold-start trouble and
reduce the length of warm-up periods. A high viscosity index will minimize changes
in viscosity with corresponding changes in temperature.
CAUTION
• Do not substitute synthetic fluids unless it has been determined that hoist,
motor and hydraulic system seals are compatible.
4
Form MHD56465 Edition 3

















