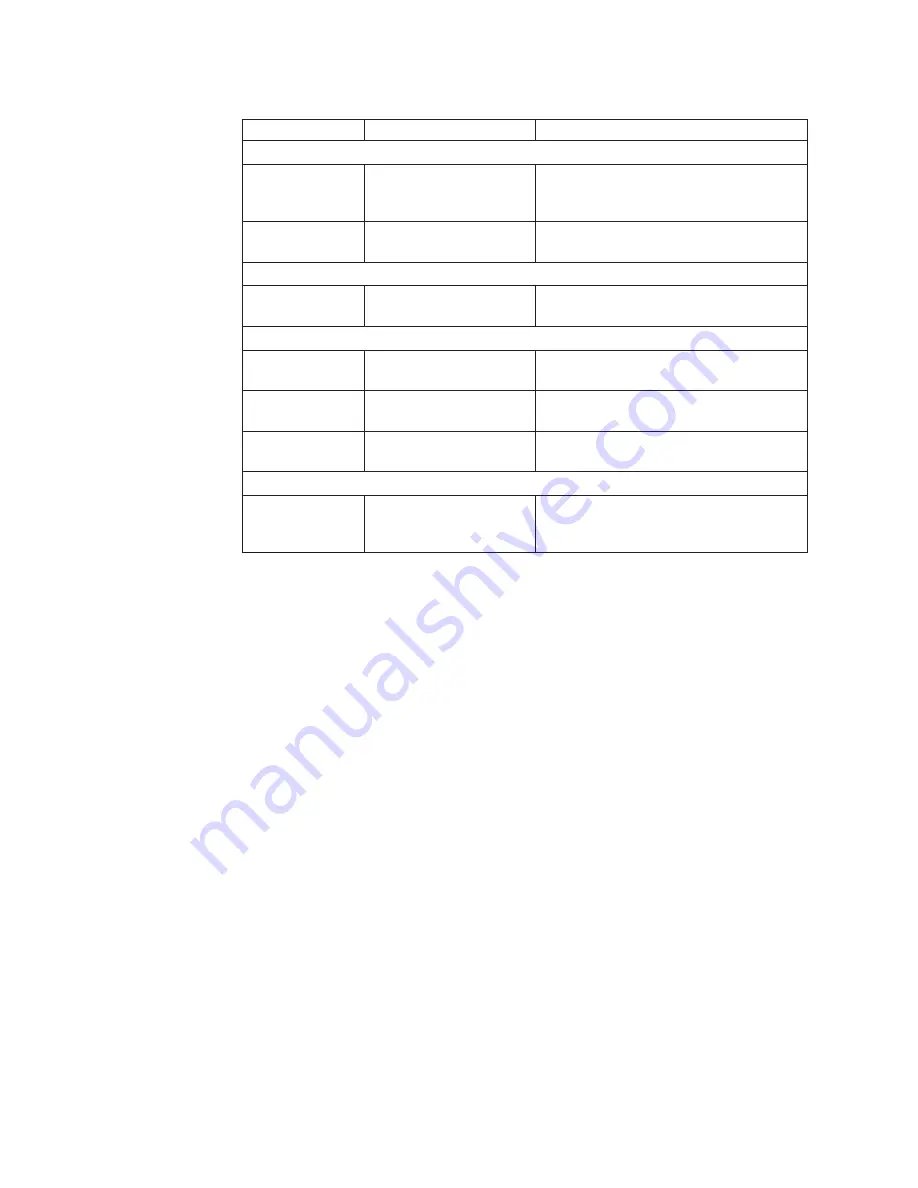
Table 7. NSBxxxx error codes and text messages (continued)
Error code
Error message
What you should do
Client IP address messages (NSB85xxx)
NSB85509
Duplicate IP address
x
%s,
that is owned by %s.
Verify your network configuration settings
in the setup utility, and the DHCP or
BOOTP server configuration settings.
NSB85519
IBM thin client IP address
not valid.
Verify your network configuration settings
in the setup utility.
Subnet mask messages (NSB86xxx)
NSB86509
Subnet mask not valid.
Verify your network configuration settings
in the setup utility.
IP address messages (NSB87xxx)
NSB87509
Address resolution failed,
IP address
x
%s.
Verify your network configuration settings
in the setup utility.
NSB87519
Address resolution failed.
IP address
x
%s not valid.
Verify your network configuration settings
in the setup utility.
NSB87529
IP address %s not in ARP
cache.
Verify your network configuration settings
in the setup utility.
Remote packet messages (NSB88xxx)
NSB88500
Stopping DLL packet
replication.
Reload the factory default settings on the
thin client, and then configure the network
settings in the setup utility.
Understanding error messages generated by the IBM NetVista
Thin Client Setup Utility
Error messages that are generated by the IBM NetVista Thin Client Setup Utility
consist of a prefix and a five digit, numeric code. The prefix for these error
messages is
NSB
. The numeric code that follows the prefix indicates the group, sub
group, message number, and message origin. For example, the error message
NSB12530
indicates an error message from group 1, sub group 2, message number
53, and a message origin of 0.
Group
Error messages can be in the following groups:
v
Group 0 indicates general messages.
v
Group 1 indicates memory-related messages.
v
Group 2 indicates multimedia messages.
v
Group 3 indicates input device messages.
v
Group 4 indicates universal serial bus (USB) device messages.
v
Group 5 indicates storage messages.
v
Group 6 indicates local area network (LAN) messages.
v
Group 7 indicates network priority messages.
v
Group 8 indicates network communication messages.
Sub group
You can classify error messages by the following subgroups:
v
Group 1 includes the following subgroups:
Common memory messages (sub group 0).
24