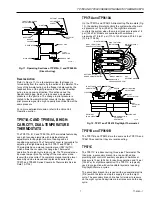
TP790 AND TP9600 SERIES PNEUMATIC THERMOSTATS
5
77-9382—1
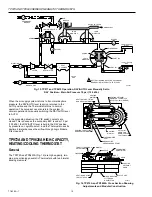
Fig. 8. TP973 and TP9630 Operating
Section—Main Port Capped.
Operation
Direct Action
Refer to Figures 7 and 8. On a temperature rise, the flapper
is forced toward the nozzle by the action of the temperature-
sensing bimetal, which reduces the flapper-nozzle gap. The
change in the flapper-nozzle gap allows less air to escape
from the nozzle, thus increasing the pressure in the nozzle
chamber as well as the branch line. The controlled device is
thereby positioned to maintain the controlled space to the
desired temperature.
The Thermostat provides a BLP that is a function of ambient
temperature. The force from the bimetal acting on the flapper
is balanced by the feedback force of the BLP acting on the
opposite side of the flapper through the nozzle. If the
setpoint knob is changed to a new setting, the opposing
MAIN LINE
TO CONTROLLED
DEVICE
BACKPLATE
RESTRICTOR
NOZZLE
NOZZLE
CHAMBER
FLAPPER
THROTTLING RANGE
ADJUSTMENT
BIMETAL
CALIBRATION
SCREW
SETPOINT
KNOB
CAM
SLOPE
SETPOINT
CAM
C6053
forces in the lever system go out of balance and the room
ambient temperature changes to rebalance the lower
system.
For example, if the setpoint cam is moved to a higher
temperature setting, the point of the lever system that rides
the slope of the cam lowers (direct-acting device) due to this
cam slope. As a result, the bimetal reduces its force applied
to the flapper. The reduced force causes the BLP to bleed
down and a heating valve to open. Heat is introduced to the
space until the forces of the bimetal are again in equilibrium
with the opposing force (8 psi [55 kPa] times the area of the
nozzle at the flapper). A reduction in setpoint causes the
reverse to happen.
The calibration screw allows for matching the bimetal start
position with the indicated setting on the setpoint cam to
achieve an 8 psi (55 kPa) BLP at the indicated setpoint.
The TR adjustment (Fig. 9) provides a means for changing
the effective length of the bimetal. When the TR adjustment
is moved over the nozzle, the force from the bimetal is
exerted directly over the nozzle and a narrow TR, or very
high sensitivity, results. For example, a 1
°
F (0.56
°
C) change
in temperature results in a 5 psi (34 kPa) BLP change.
When the TR adjustment is moved toward the end of the
bimetal away from the nozzle, the effective force output of
the bimetal is reduced. This reduction requires a greater
temperature change at the bimetal to throttle the flapper over
the nozzle. The result is a wider TR or very low sensitivity; for
instance, a 1
°
F (0.56
°
C) change in temperature results in
only a 1 psi (7 kPa) BLP change.
Reverse Action
Refer to Figures 7 and 8. On a temperature rise, the flapper
is forced away from the nozzle by the action of the
temperature-sensing bimetal, which increases the flapper-
nozzle gap. The change in the flapper-nozzle gap allows
more air to escape from the nozzle, thus decreasing the
pressure in the nozzle chamber as well as the branch line.
The controlled device is thereby positioned to maintain the
controlled space to the desired temperature.
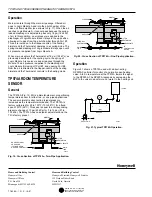
Fig. 9. Cross Section of TP973 and TP9630 Thermostat.
BIMETAL
RESTRICTOR
MAIN
LINE
BRANCH
LINE
NOZZLE
FLAPPER
C6054
FILTER
BRANCHLINE
PRESSURE
GAGE TAP
THROTTLING
RANGE
ADJUSTMENT
CALIBRATION
SCREW
SETPOINT
CAM
SETPOINT
KNOB