--- 15 ---
Front cap
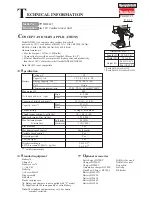
8-3. Structure of the DH 25PA and DH 25PB Hammer Drills
Grip
Needle pin
Cylinder
Steel ball
Second
hammer
Striker
Air chamber
Third
gear
Piston
Connecting
rod
Crank shaft
First gear
Key rail
(2 pieces)
Retainer
sleeve
O-ring
Second gear
Third pinion
Armature
Handle
Fig. 2
Transmission of rotation
Transmission of rotation is described with reference to Fig. 2. The gear arrangement of the Models DH 25PA
and DH 25PB is the same as that of Model DH 20V.
Rotation of the armature is transmitted to the second gear to rotate the third gear via the slip mechanism
between the second gear and the third pinion shaft. Rotation of the third gear is then transmitted to the
cylinder threaded onto the third gear. Rotation of the cylinder is transmitted to the retainer sleeve coupled
together by means of three needle pins, and then to the drill bit inserted into the retainer sleeve by way of two
key rails and a steel ball which hold the bit.
Striking function
Rotation of the armature is transmitted to the crank shaft and the connecting rod, and the piston reciprocates
within the cylinder. As the piston reciprocates, the changing air pressure inside the air chamber between the
piston and the striker causes the striker to move and continuously strike against the end of the second
hammer. At the same time, the changing air pressure within the air chamber which moves the striker also
provides an "air cushion" which absorbs the impact of the striking action.