GENERAL INFORMATION
- 27 -
hose, do not exert excessive force on the hose or fitting. Remove the hose clamp and carefully insert a
small screwdriver or pick tool between the fitting and hose. Apply a spray lubricant under the hose and
carefully twist the hose off the fitting. Clean the fitting of any corrosion or rubber hose material with a
wire brush Clean the inside of the hose thoroughly. Do not use any lubricant when installing the hose
(new or old). The lubricant may allow the hose to come off the fitting, even with the clamp secure.
Bearings
Bearings are used in the engine and
transmission assembly to reduce power loss, heat
and noise resulting from friction. Because bearings
are precision parts, they must be maintained with
proper lubrication and maintenance. If a bearing is
damaged, replace it immediately. When installing a
new bearing, take care to prevent damaging it.
Bearing replacement procedures are included in the individual chapters where applicable; however.
Use the following sections as a guideline.
NOTE
Unless otherwise specified, install bearings with the
manufacturer’s mark or number facing outward.
Removal
While bearing are normally removed only when
damaged, there may be times when it is necessary to
remove a bearing that is in good condition. However,
improper bearing removal will damage the bearing and
possibly the shaft or case. Note the following when
removing bearings:
1. When using a puller to remove a bearing from a
shaft, take care that the shaft is not damaged.
Always place a piece of metal between the end
of the shaft and the puller screw. In addition,
place the puller arms next to the inner bearing
race. See Figure 42.
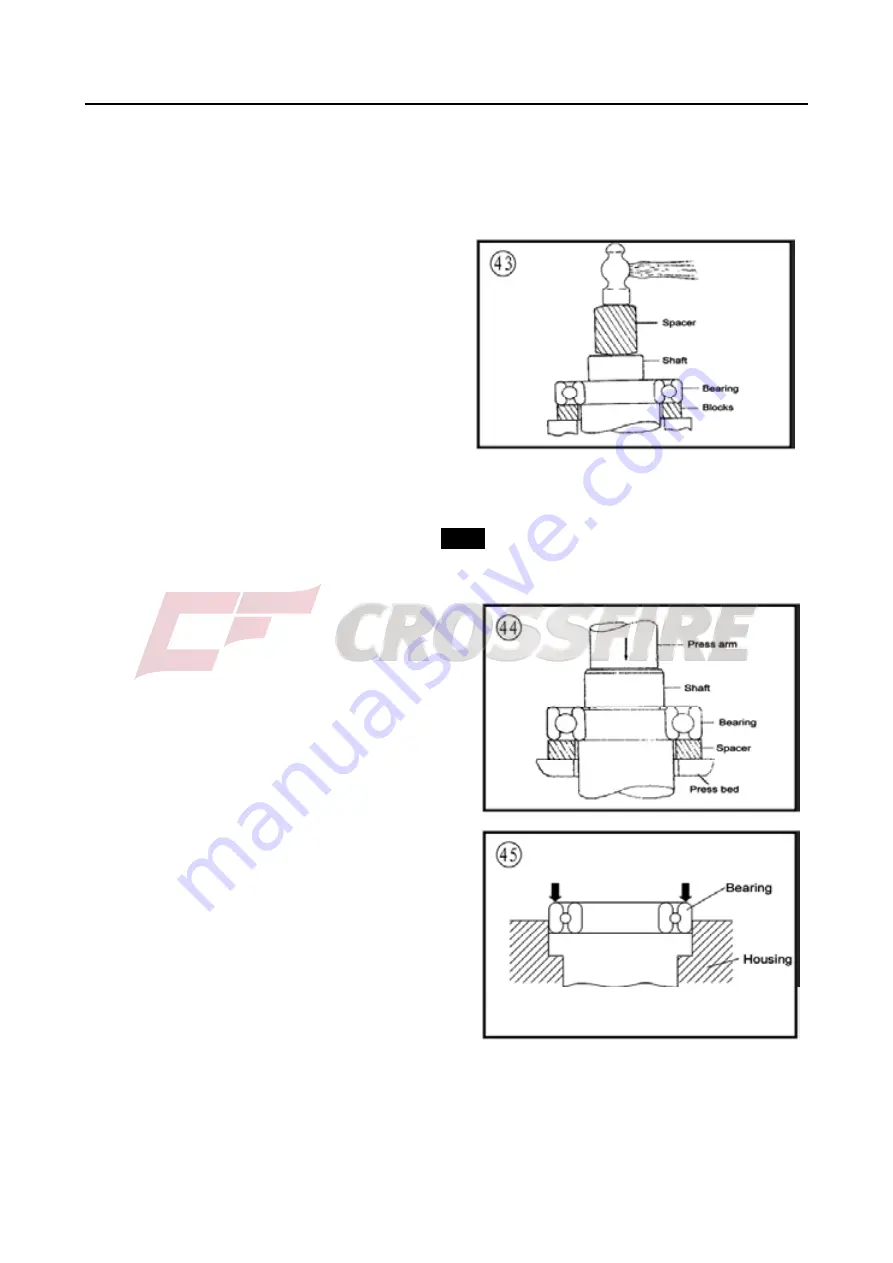
2. When using a hammer to remove a bearing from
a shaft. do not strike the hammer directly against
the shaft. Instead, use a brass or aluminum rod
between the hammer and shaft (Figure 43) and
make sure to support both bearing races with wooden blocks as shown.
3. The ideal method of bearing removal is with a hydraulic press. Note the following when using a
press:
a. Always support the inner and outer bearing races with a suitable size wooden or aluminum
spacer (Figure 44). If only the outer race is supported, pressure applie against the balls