Wireless Access Point
HNW150AP
User Manual
165
Diagnosing Problem using IP Utilities
ping
Ping
is a command you can use to check whether your PC can recognize other computers on your network
and the Internet. A ping command sends a message to the computer you specify. If the computer receives
the message, it sends messages in reply. To use it, you must know the IP address of the computer with
which you are trying to communicate.
On Windows-based computers, you can execute a ping command from the Start menu. Click the
Start
button, and then click
Run
. In the
Open
text box, type a statement such as the following:
ping 192.168.1.254
Click
OK
. You can substitute any private IP address on your LAN or a public IP address for an Internet site,
if known.
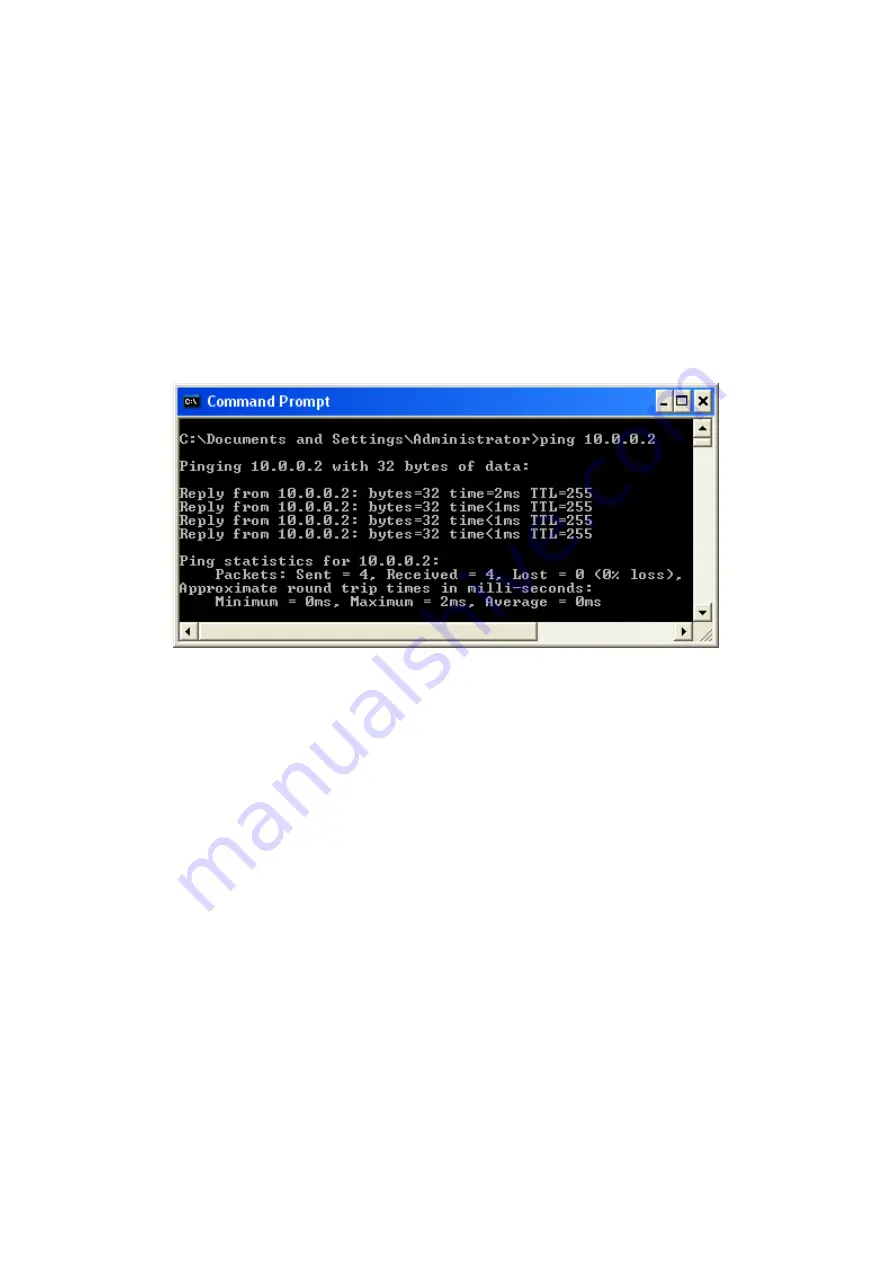
If the target computer receives the message, a
Command Prompt
window is displayed:
Figure 11:
Using the ping Utility
If the target computer cannot be located, you will receive the message
Request timed out
.
Using the ping command, you can test whether the path to the Wireless Gateway is working (using the
preconfigured default LAN IP address 192.168.1.254) or another address you assigned.
You can also test whether access to the Internet is working by typing an external address, such as that for
www.yahoo.com
(216.115.108.243). If you do not know the IP address of a particular Internet location, you
can use the
nslookup
command, as explained in the following section.
From most other IP-enabled operating systems, you can execute the same command at a command
prompt or through a system administration utility.
nslookup
You can use the nslookup command to determine the IP address associated with an Internet site name.
You specify the common name, and the nslookup command looks up the name in on your DNS server
(usually located with your ISP). If that name is not an entry in your ISP’s DNS table, the request is then
referred to another higher-level server, and so on, until the entry is found. The server then returns the
associated IP address.
On Windows-based computers, you can execute the nslookup command from the
Start
menu. Click the
Start
button, and then click
Run
. In the
Open
text box, type the following:
nslookup
Click
OK
. A Command Prompt window displays with a bracket prompt (>). At the prompt, type the name of
the Internet address that you are interested in, such as
www.microsoft.com
.
The window will display the associate IP address, if known, as shown below:






















