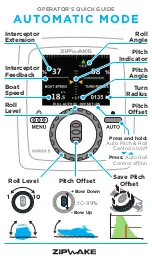
10
Subject to change without notice
with approximately constant group delay (therefore good pulse
transmission performance) the following numerical relationship
between rise time tr (in ns) and bandwidth B (in MHz) applies:
Connection of Test Signal
In most cases briefly depressing the AUTO SET causes a useful
signal related instrument setting. The following explanations
refer to special applications and/or signals, demanding a manual
instrument setting. The description of the controls is explained
in the section “controls and readout”.
Caution:
When connecting unknown signals to the oscilloscope
input, always use a x10 probe, automatic triggering
and set the input coupling switch to DC (readout). The
attenuator should initially be set to 20V/div.
Sometimes the trace will disappear after an input signal has
been applied. Then a higher deflection coefficient (lower input
sensitivity) must be chosen until the vertical signal height is
only 3-8div. With a signal amplitude greater than 160Vpp and
the deflection coefficient (
VOLTS/DIV.
) in calibrated condition,
an attenuator probe must be inserted before the vertical input.
If, after applying the signal, the trace is nearly blanked, the
period of the signal is probably substantially longer than the set
time deflection coefficient (
TIME/DIV.
). It should be switched
to an adequately larger time coefficient.
The signal to be displayed can be connected directly to the Y-
input of the oscilloscope with a shielded test cable such as
HZ32
or
HZ34
, or reduced through a x10 or x100 attenuator probe. The
use of test cables with high impedance circuits is only
recommended for relatively low frequencies (up to approx.
50kHz). For higher frequencies, the signal source must be of low
impedance, i.e. matched to the characteristic resistance of the
cable (as a rule 50
Ω
). Especially when transmitting square and
pulse signals, a resistor equal to the characteristic impedance
of the cable must also be connected across the cable directly
at the Y-input of the oscilloscope. When using a 50
Ω
cable such
as the
HZ34
, a 50
Ω
through termination type
HZ22
is available
from
HAMEG
. When transmitting square signals with short rise
times, transient phenomena on the edges and top of the signal
may become visible if the correct termination is not used. A
terminating resistance is sometimes recommended with sine
signals as well. Certain amplifiers, generators or their attenuators
maintain the nominal output voltage independent of frequency
only if their connection cable is terminated with the prescribed
resistance. Here it must be noted that the terminating resistor
HZ22
will only dissipate a maximum of 2Watts. This power is
reached with 10Vrms or at 28.3Vpp with sine signal. If a x10 or
x100 attenuator probe is used, no termination is necessary. In
this case, the connecting cable is matched directly to the high
impedance input of the oscilloscope. When using attenuators
probes, even high internal impedance sources are only slightly
loaded (approx. 10M
Ω
II 12pF or 100M
Ω
II 5pF with
HZ53
).
Therefore, if the voltage loss due to the attenuation of the probe
can be compensated by a higher amplitude setting, the probe
should always be used. The series impedance of the probe
provides a certain amount of protection for the input of the
vertical amplifier. Because of their separate manufacture, all
attenuator probes are only partially compensated, therefore
accurate compensation must be performed on the oscilloscope
(see Probe compensation ).
Standard attenuator probes on the oscilloscope normally reduce
its bandwidth and increase the rise time. In all cases where the
oscilloscope bandwidth must be fully utilized (e.g. for pulses
pressed X-MAG. (x10) button: Tc = 0.05µs/div,
required rec. freq. F = 1:(0.8x0.05x10
-6
) = 25MHz,
required period T = 1:(25x10
6
) = 40ns
.
If the time is relatively short as compared with the complete
signal period, an expanded time scale should always be applied
(X-MAG. (x10) active). In this case, the time interval of interest can
be shifted to the screen center using the X-POS. control.
When investigating pulse or square waveforms, the critical
feature is the risetime of the voltage step. To ensure that
transients, ramp-offs, and bandwidth limits do not unduly influence
the measuring accuracy, the risetime is generally measured
between 10% and 90% of the vertical pulse height. For
measurement, adjust the Y deflection coefficient using its varia-
ble function (uncalibrated) together with the Y-POS. control so
that the pulse height is precisely aligned with the 0% and 100%
lines of the internal graticule. The 10% and 90% points of the
signal will now coincide with the 10% and 90% graticule lines.
The risetime is given by the product of the horizontal distance in
div between these two coincident points and the calibrated time
coefficient setting. The fall time of a pulse can also be measured
by using this method.
The following figure shows correct positioning of the oscilloscope
trace for accurate risetime measurement.
With a time coefficient of 10ns/div (X x10 magnification active),
the example shown in the above figure results in a total measured
risetime of
t
tot
= 1.6div x 10ns/div = 16ns
When very fast risetimes are being measured, the risetimes of
the oscilloscope amplifier and of the attenuator probe has to be
deducted from the measured time value. The risetime of the
signal can be calculated using the following formula.
In this t
tot
is the total measured risetime, t
osc
is the risetime of the
oscilloscope amplifier (approx. 8.75ns), and t
p
the risetime of the
probe (e.g. = 2ns). If t
tot
is greater than 100ns, then t
tot
can be taken
as the risetime of the pulse, and calculation is unnecessary.
Calculation of the example in the figure above results in a
signal risetime
t
r
=
√
16
2
- 8.75
2
- 2
2
= 13.25ns
The measurement of the rise or fall time is not limited to the trace
dimensions shown in the above diagram. It is only particularly simple
in this way. In principle it is possible to measure in any display position
and at any signal amplitude. It is only important that the full height
of the signal edge of interest is visible in its full length at not too great
steepness and that the horizontal distance at 10% and 90% of the
amplitude is measured. If the edge shows rounding or overshooting,
the 100% should not be related to the peak values but to the mean
pulse heights. Breaks or peaks (glitches) next to the edge are also
not taken into account. With very severe transient distortions, the
rise and fall time measurement has little meaning. For amplifiers
Type of signal voltage