59
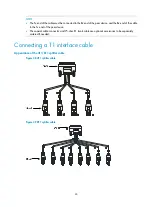
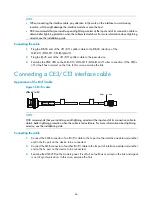
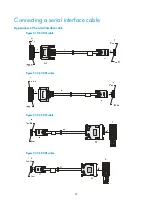
Connecting interface cables
Connecting an Ethernet interface cable
Appearance of an Ethernet cable
Figure 38
Ethernet cable
10/100 Mbps Ethernet uses category-5 twisted pair cables, while 1000 Mbps Ethernet uses category-5
enhanced or category-6 twisted pair cables. Twisted pair cables include straight-through cables and
crossover cables.
Category-5 cables provide a transmission frequency of 100 MHz for voice and data transmission; they
are mainly used in 100Base-T and 10Base-T networks. Category-5 cables are common Ethernet cables,
which can also be used to transmit 1000 Mbps Ethernet data.
Category-5 enhanced cables feature low attenuation and crosstalk, providing higher attenuation to
crosstalk ratio (ACR), less delay error and higher performance than category-5 cables. Category-5
enhanced cables are mainly used in 1000 Mbps Ethernet networks.
Category-6 cables provide a transmission frequency of 1 MHz to 250 MHz, and improve the
performance on crosstalk and return loss. A fine better return loss performance is extremely important for
new-generation full-duplex high-speed networks. Category-6 cables have sufficient power sum ACR
(PS-ACR) when working at 200 MHz. They provide a bandwidth two times than that of category-5
enhanced cables, thus featuring a higher transmission performance. Therefore, category-6 cables are
suitable for applications requiring a transmission speed of more than 1 Gbps.
The 10/100 Mbps Ethernet uses two pairs of cables, orange/white, orange, green/white and green
cables, to transmit and receive data, while the 1000 Mbps Ethernet uses four pairs of cables to transmit
and receive data.
For the pinouts of common twisted pair cables, see the following tables. (A and B represent the two ends
of a cable.)
Table 72
Straight-through cable pinouts
Pinout No.
A
B
1 Orange/white
Orange/white
2 Orange
Orange
3 Green/white
Green/white
4 Blue Blue
5 Blue/white
Blue/white
6 Green
Green
7 Brown/white
Brown/white