Operation Manual – MSTP
H3C S9500 Series Routing Switches
Chapter 1 MSTP Configuration
1-17
Role
State
Root
port/Master
port
Designated
port
Alternate
port
Backup port
Discarding
√
√
√
√
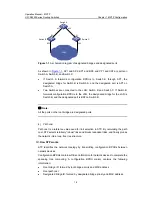
III. How MSTP works
MSTP divides an entire Layer 2 network into multiple MST regions, which are
interconnected by a computed CST. Inside an MST region, multiple spanning trees are
generated through computing, each spanning tree called an MSTI. Among these
MSTIs, instance 0 is the IST, while all the others are MSTIs. Similar to STP, MSTP uses
configuration BPDUs to compute spanning trees. The only difference between the two
protocols being in that what is carried in an MSTP BPDU is the MSTP configuration on
the device from which this BPDU is sent.
1) CIST
calculation
By comparison of configuration BPDUs, one device with the highest priority is elected
as the root bridge of the CIST. MSTP generates an IST within each MST region through
computing, and, at the same time, MSTP regards each MST region as a single device
and generates a CST among these MST regions through computing. The CST and
ISTs constitute the CIST of the entire network.
2) MSTI
calculation
Within an MST region, MSTP generates different MSTIs for different VLANs based on
the VLAN-to-MSTI mappings.
MSTP performs a separate computing process, which is similar to spanning tree
computing in STP, for each spanning tree. For details, refer to
How STP works
in
section 1.1.1.
In MSTP, a VLAN packet is forwarded along the following paths:
z
Within an MST region, the packet is forwarded along the corresponding MSTI.
z
Between two MST regions, the packet is forwarded along the CST.
IV. Implementation of MSTP on devices
MSTP is compatible with STP and RSTP. STP and RSTP protocol packets can be
recognized by devices running MSTP and used for spanning tree computing.
In addition to basic MSTP functions, many management-facilitating special functions
are provided, as follows:
z
Root bridge hold
z
Root bridge backup
z
Root guard
z
BPDU guard
z
Loop guard