17
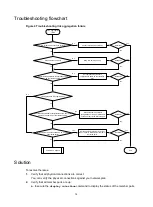
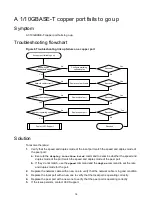
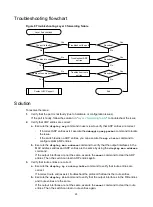
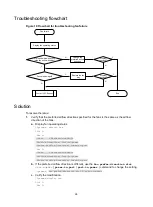
1.
Verify that the speed and duplex mode of the local port match the speed and duplex mode of
the peer port:
a.
Execute the
display interface brief
command to examine whether the speed and
duplex mode of the port match the speed and duplex mode of the peer port.
b.
If they do not match, use the
speed
command and the
duplex
command to set the rate
and duplex mode for the port.
2.
Verify that the speed and duplex mode of the local port match the speed and duplex mode of
the transceiver module:
a.
Execute the
display interface brief
command to examine whether the speed and
duplex mode of the port match the speed and duplex mode of the transceiver module.
b.
If they do not match, use the
speed
command and the
duplex
command to set the rate
and duplex mode for the port.
3.
Verify that the ports at both ends are operating correctly:
a.
For a 10-GE SFP+ fiber port, use an SFP+ cable (used for short-haul connection) to directly
connect it to another 10-GE SFP+ fiber port on the local end. For a 40-GE QSFP+ port, use
a QSFP+ cable (used for short-haul connection) to directly connect it to another 40-GE
QSFP+ port on the local end.
b.
Identify whether the port can go up:
−
If the port can go up, you can determine that the peer port fails. Replace the peer port
with a new port operating correctly.
−
If the port cannot go up, you can determine that the local port fails. Replace the local port
with a new port operating correctly.
4.
Verify that the transceiver module and cable are operating correctly:
a.
Use the
display transceiver alarm interface
command to display the alarms
present on the transceiver module:
−
The device displays
None
if no error occurs.
−
The device displays alarms if the transceiver module fails or the type of the transceiver
module does not match the port type.
b.
Use an optical power meter to verify that the Tx power and Rx power of the transceiver
module are stable and are within the correct range.
c.
Execute the
display transceiver interface
command to verify that the wavelength
and transmission distance of the local transceiver module are consistent with the
wavelength and transmission distance of the peer transceiver module.
d.
If the transceiver module is not operating correctly, replace it with a H3C transceiver module
that matches the fiber port.
For more information about transceiver modules and cables, see the installation guide.
NOTE:
When you use a QSFP+ to SFP+ cable to connect a 40-GE QSFP+ fiber port, you must use an
optical attenuator because the Tx optical power of the QSFP+ transceiver module exceeds the
upper Rx optical power limit of the SFP+ transceiver module.
5.
Verify that the fiber matches the transceiver module. If they do not match, replace the fiber with
a new one that matches the transceiver module.
For more information about fibers, see the installation guide.
6.
If the issue persists, contact H3C Support, and provide the following information:
<H3C> display diagnostic-information
Save or display diagnostic information (Y=save, N=display)? [Y/N]:Y