Use a damp cloth to clean plastic parts. Do
not use any cleaners, solvents or sharp
objects.
Free the vent holes and movable parts of any
deposited dust with a soft brush or tweezers
after each use.
Lubricate all movable parts regularly.
Hose set maintenance (pic. 2)
Regular maintenance needs to be executed for
perfect function of the hoses.
The gas nozzle needs to be regularly sprinkled
by protective nozzle spray and freed of deposits
inside.
The following steps need to be taken for this
case (see pic. 2):
5. Remove the nozzle (1) by pulling forward.
6. Free the nozzle of any deposits formed by
the weld cinder.
7. Sprinkle it with protective nozzle spray.
8. If the nozzle is rusty, it needs to be replaced.
Current nozzle maintenance
The following steps need to be taken for this
case (see pic. 2):
5. Remove the nozzle (1) by pulling forward.
6. Unscrew the current nozzle (2)
7. Check whether the hole the wire goes
through is not too wide or, in case of need,
replace it before reassembly.
8. Press the button on the hose so that the wire
protruded and remount the current nozzle.
Nozzle holder maintenance
The following steps need to be taken for this
case (see pic. 2):
1.
Holes for gas drainage can sometimes be
slightly stuffed, in such a case the gas
nozzle needs to be disassembled by
pulling (1),
2.
Unscrew then the current nozzle and gas
distributor and replace with a new one.
Attention!!! Execute the hose set
maintenance regularly (blow and clean the
wire guidance tube, wire feed pulley, gas
nozzle and gas distributor).
Safety instructions for
inspection and maintenance
Only a regularly maintained and treated
appliance can become a reliable helper.
Insufficient care and maintenance can be a
cause of unpredictable accidents and injuries.
Follow all safety instructions mentioned in these
Operating Instructions.
Tip for welding
The welded zone should be free of rust and
varnish. The torch is selected according to
material type. We recommend first trying the
current strength on a waste piece.
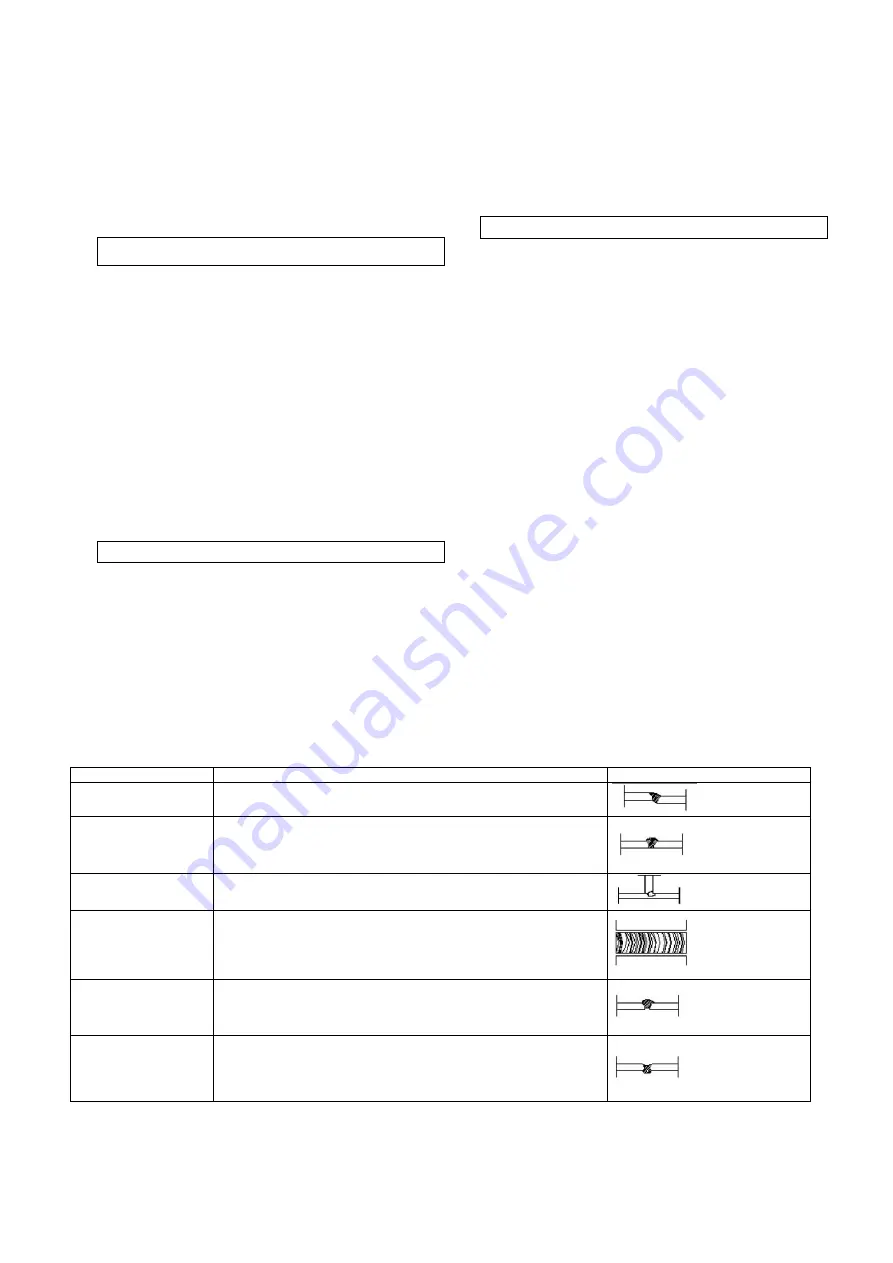
Failure
Cause and remedy
Example
The processed piece is
awry
3.
Poor seam preparation
4.
Straighten the edges and fix them to the welding
Weld elevation
5.
Idle run voltage is too low
6.
Welding speed is too low
7.
Faulty adjacent angle of the welding torch
8. Too
strong
wire
Small metal layer
3.
Welding is too quick
4.
Too low voltage for welding speed
Welds have oxidised
appearance
5.
Weld in a pit with a long electric arc
6.
Set the voltage
7.
The wire is crooked or it excessively protrudes from the wire
guidance
8.
Faulty wire feed speed
Insufficient root welding
5.
Irregular or insufficient distance
6.
Faulty adjacent angle of the welding torch
7.
Worn-out wire guidance tube
8.
Wire feed or welding speed is too low
Penetration
4.
Wire feed speed is too high
5.
Faulty adjacent angle of the welding torch
6.
Too long distance






























