Bit Pad Two 18
Each characteristic or function and its commands are defined. For easy reference, the
commands appear in ASCII and hexadecimal.
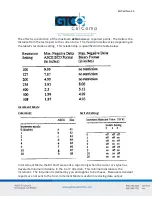
Appendix B ASCII Conversion Chart
also
provides the binary, decimal and octal conversions. A summary of the commands and
switch settings appears in
Appendix D Quick Reference Sheet
.
The command byte format uses the same conventions as those used in the report formats:
one start bit, seven data bits, an optional parity bit and one or two stop bits.
Commands are one byte long. The Bit Pad Two command buffer can hold ten bytes;
therefore, up to ten bytes can be sent to the Bit Pad Two in quick succession.
Section A: Controlling the Report Flow and Content
Use the operating characteristics described in the section to control when reports are
issued, how fast they are issued and coordinate content. Furthermore, reports can be
gated (allowed to flow or not) with the
Start
and
Stop Transmission
commands.
Some characteristics are called
modifiers
because they can be combined with
primary
modes
. The primary modes are Stream, Switch Stream, Point and Remote Request modes.
The modifiers are Absolute, Relative and Increment modes, as well as Report Rate.
Primary Modes: Stream, Switch Stream Modes and Report Rate
Command
Summary of Contents for BIT PAD TWO DATA
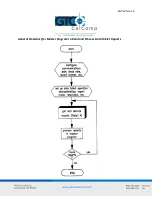
Page 14: ...Bit Pad Two 14 General Flowchart for Master Program to Read and Process Data Tablet Reports...
Page 15: ...Bit Pad Two 15 Detail A Get and Decode Reports Subroutine...
Page 16: ...Bit Pad Two 16 Detail B Data Input Subroutine...
Page 34: ...Bit Pad Two 34...
Page 42: ...Bit Pad Two 42 Appendix B ASCII Conversion Chart...
Page 43: ...Bit Pad Two 43...
Page 44: ...Bit Pad Two 44...
Page 46: ...Bit Pad Two 46 Switch Settings DIP Switch 1...