9
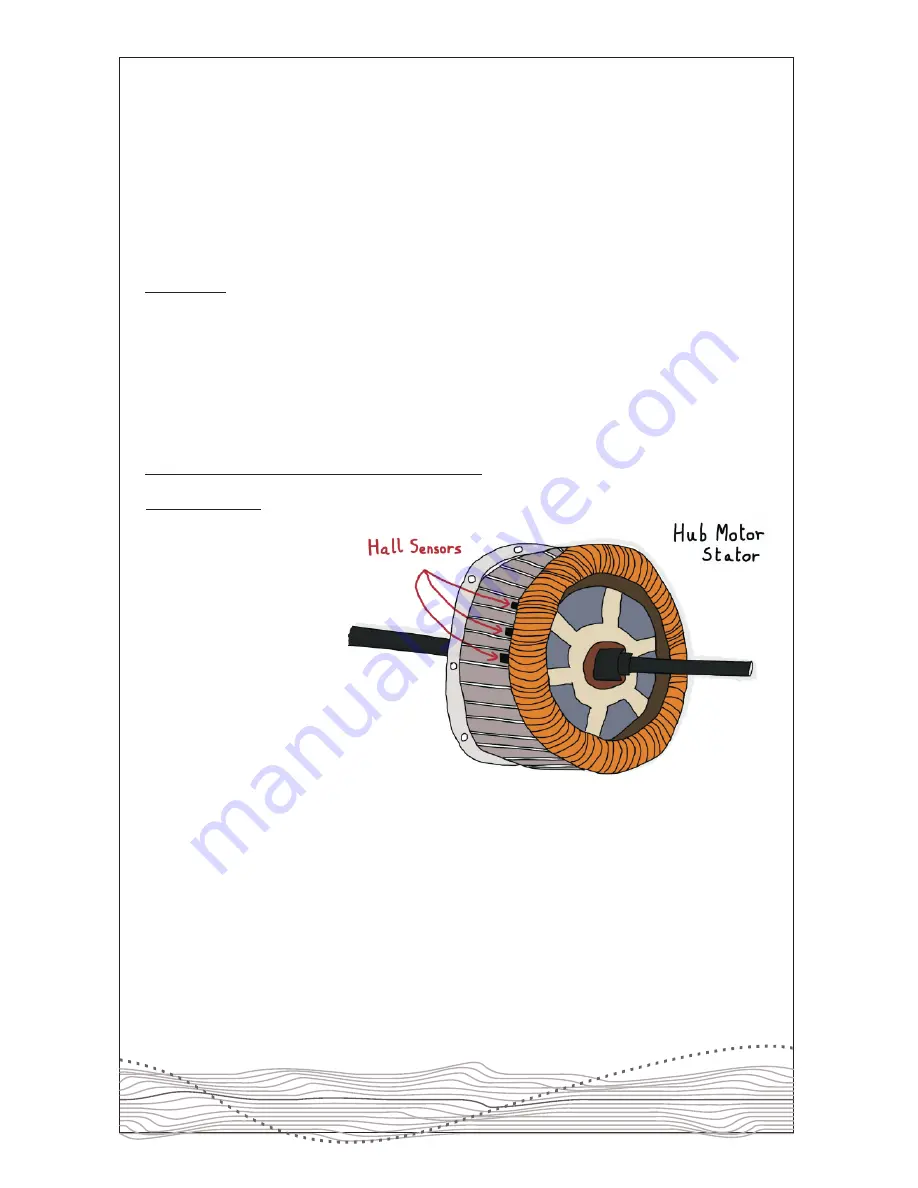
In modern direct drive hub
motors the current is
supplied sequentially to the
three different "phase"
wires coming from the
motor (normally visible as
thick green, blue and yellow
wires coming from the hub)
to make the motor spin
forwards correctly.
However, when the motor is
stationary the controller can have a hard time figuring out the order in which to supply the
current. The hall sensor is a small chip inside the motor (there are typically 3 of them)
which sends a signal to the motor controller to help it figure out the order. If a hall sensor
is defective it can lead to the characteristic stuttery behaviour seen from the motor.
For example, a 36V Lithium Manganese (LiMn) battery is 42V when hot off the charger,
whilst it will tend to operate around 36-38V for most of the discharge. A 48V Lithium Iron
Phosphate (LiFePO4) can be as high as 60V at the end of charging but will normally
operate around 48-52V whilst discharging.
It should also be noted that the more you discharge a lithium battery at higher rates the
shorter the total lifespan of the battery will tend to be even if you are discharging within the
manufacturer’s recommended discharge rating.
The C rating is a way to rate the battery's ability to discharge at particular currents, relative
to its capacity. For example, if the battery's cells are rated for a 2C discharge, and the
battery is a 10Ah battery, then the recommended maximum discharge rate is 2(C) x 10(Ah)
which comes out to 20A. Discharges at current levels above the recommended C rating
risk damaging the cells and reducing their total cycle life.
C Rating:
Motor/Motor Controller Terminology:
Hall Sensors:





























