14.4
PID Algorithm Selection (PIDISA or PIDIND) and Gain
Calculations
The PID function supports both the Independent Term (PID_IND) and ISA standard
(PID_ISA) forms of the PID algorithm. The Independent Term form takes its name from
the fact that the coefficients for the proportional, integral and derivative terms act
independently. The ISA algorithm is named for the Instrument Society of America (now
the International Society for Measurement and Control), which standardized and
promoted it.
The two algorithms differ in how words 6 through 8 of the reference array are used and in
how the PID output (CV) is calculated.
The Independent term PID (PID_IND) algorithm calculates the output as:
PID Output = Kp * Error + Ki * Error * dt + Kd * Deri CV Bias
where Kp is the proportional gain, Ki is the integral rate, Kd is the derivative time, and dt
is the time interval since the last solution.
The ISA (PID_ISA) algorithm has different coefficients for the terms:
PID Output = Kc * (Error + Error * dt/Ti + Td * Derivative) + CV Bias
where Kc is the controller gain, Ti is the Integral time and Td is the Derivative time. The
advantage of PID_ISA is that adjusting Kc changes the contribution for the integral and
derivative terms as well as the proportional term, which can simplify loop tuning.
If you have the PID_ISA Kc, Ti and Td values, use the following equations to convert
them to use as:PID_IND parameters:
Kp = Kc, Ki = Kc/Ti, and Kd = Kc * Td
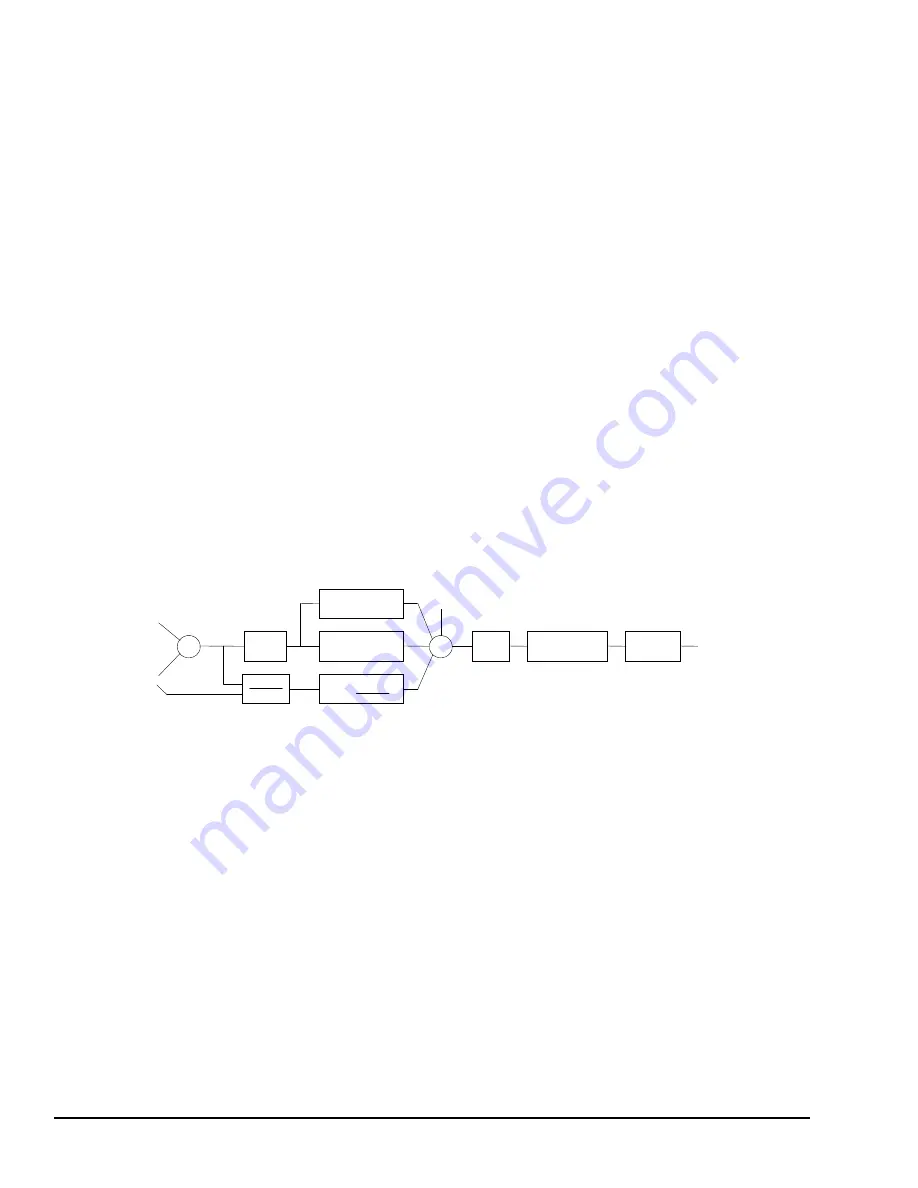
The following diagram shows how the PID_IND algorithm works:
Ki
*
Error
*
∆
Time
Integral Term =
Proportional Term =
Kp
*
Error
Dead
Band
CV
Bias
Slew
Limit
Clamp
Upper / Lower
Polarity
CV
SP
PV
Error Term Sign
Deriv Action
+/-
∆
Value
∆
Time
Derivative Term =
∆
Time
Kd
*
∆
Value
-/+
+
Previous Integ. Term +
The ISA Algorithm (PID_ISA) is similar except that its Kc gain coefficient is applied
after the three terms are summed, so that the integral gain is Kc / Ti and the derivative
gain is Kc * Td.
Bits 0, 1 and 2 in the Config Word set the Error sign, Output Polarity and Derivative
Action, respectively.
14.4.1
Error Term
Both PID algorithms calculate the Error term as
Error = (SP – PV),
which can be changed to Reverse Acting mode:
Error = (PV – SP)
by setting the Error Term mode (bit 0) in the Config Word – (word 13 of the reference
array) to 1.
Reverse -Acting mode is used if you want the CV output to move in the opposite direction
from PV input changes (CV down for PV up) instead of the normal CV up for PV up.
284
GFK-1503E
VersaMax PLC User Manual
For public disclosure
Summary of Contents for VersaMax PLC
Page 16: ...Notes 16 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 38: ...Notes 38 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 50: ...Notes 50 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 92: ...Notes 92 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 112: ...Notes 112 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 224: ...Notes 224 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 292: ...Notes 292 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 316: ...Notes 316 GFK 1503E VersaMax PLC User Manual For public disclosure ...
Page 317: ......
















































