RAIM: R
eceiver
A
utonomous
I
ntegrity
M
onitoring. A
method of predicting possible system accuracy errors
that may be caused by bad satellite data. The RAIM
algorithm requires that more satellites are available and
usable than required for a normal GPS position fix.
Range:
The distance from the present position to a
destination waypoint.
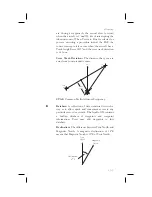
Relative Bearing Indicator:
The Relative Bearing
Indicator is an arrow next to the Bearing value that
indicates an approximate bearing to a waypoint or
airspace relative to the aircraft’s current track when
your current ground speed is more than 5 knots.
RW:
Runway Fix. A code appended to a waypoint in
the database that may not appear on a published map.
S
Second:
1/60th of a minute of a degree.
Seed Position:
A latitude and longitude position fix
approximately equal to the current position that the
Apollo GX uses to determine the location of available
satellites from which signals may be received.
Selective Availability (SA):
The degradation of
accuracy of GPS position fix data by the United States
Department of Defense for civilian use.
Space Vehicle (SV):
A GPS satellite.
Statute Mile:
A distance measurement equal to 5,280
feet or 0.87 of a nautical mile.
T
Three-dimensional (3D) Position Fix:
A position fix
defined by latitude, longitude, and altitude.
15-9
Glossary
Summary of Contents for Apollo GX50
Page 1: ......
Page 194: ...9 4 Approach Basics GX50 60...
Page 232: ...9 42 Approach Examples...
Page 240: ...9 50 Approach Examples...
Page 245: ...9 55 Approach Examples...
Page 266: ...Notes 9 76 Approach Examples...
Page 271: ...Charts have been reduced for illustrative purposes 9 81 Approach Notes...
Page 275: ...Reduced for illustrative purposes 9 85 Approach Notes...
Page 276: ...Charts have been reduced for illustrative purposes 9 86 Approach Notes...
Page 326: ...Notes 15 12 Glossary...
Page 335: ......