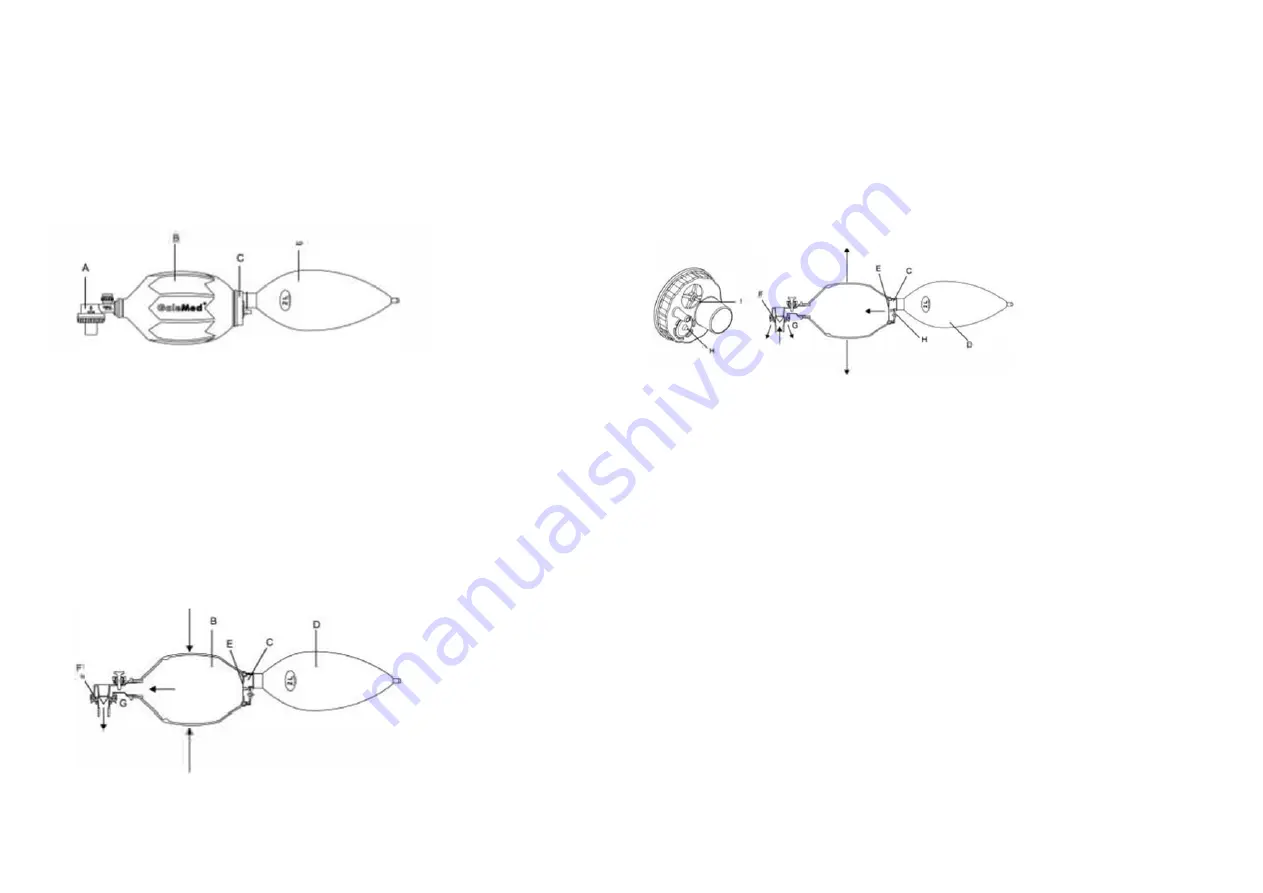
Principles Of Operation 1
The MR‐100
™
Plus Manual Resuscitator consists of four major components
(figure 1): non rebreathing valve assembly (A), silicone bag (B), intake valve
(C), and reservoir (D), Part D should be removed if supplemental oxygen is
not to be supplied from an external gas source.
Figure 1. The MR100
TM
Plus Manual Resuscitator
Gas is delivered to the patient by squeezing the bag (see figure 2). Positive
pressure within the bag caused by its compression closes the intake valve (E)
located at the base of the bag. This causes the duckbill valve (F) to close off
the expiration ports(G) of the non‐rebreathing assembly. Further
compression of the bag forces gas through duckbill valve to the patient. If
supplemental gas is used, oxygen is delivered to the reservoir (D) during
compression of the silicone bag.
Figure 2. Exhalation
Principles Of Operation 2
Exhalation begins when the patient exerts positive pressure (during passive
exhalation) on the patient side of the duckbill valve (F) or when the operator
releases pressure from the silicone bag (8). The valve lifts directing the
patient's expiratory gases through the expiration ports(G) of the non‐
rebreathing valve (see figure 3).
Figure 3. lnspiration
The silicone bag refills for the next breath during patient exhalation.
Negative pressure within the bag (caused by the expansion of the
compressed bag) opens the intake valve (E), allowing gas to enter the bag
either from the atmosphere or from the reservoir (D).
The reservoir should be used whenever supplemental oxygen Is delivered.
(Supplemental oxygen may be administered without using the reservoir but
maximum available oxygen concentration will be reduced.) Excess oxygen
vents to the atmosphere through the safety valve
(H) should the reservoir fill before the next delivered breath. If the volume of
gas in the reservoir is inadequate to fill the silicone bag, room air may be
drawn in through the reservoir valve safety inlet (I). The concentration of the
oxygen‐enriched gas entering from the reservoir will depend on factors such
as oxygen now rate, tidal volume, ventilation rate and operator technique.














