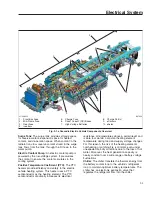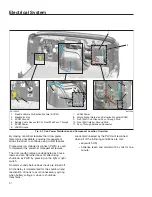
Electric Vehicle Overview
DANGER
Service and repair of an electric vehicle should
only be performed by technicians that have
completed HV3 Daimler Safety Training. To
prevent personal injury or death, or damage to
the electric system, do not attempt repairs
yourself.
WARNING
The strong electromagnetic field generated by
the inverter can cause severe personal injury or
death to people with active implanted cardiac
devices. Individuals with an active implanted
cardiac device must stay away from the vicinity
of the active equipment.
See
for an overview of the eCascadia
electric vehicle components.
See
for a diagram of a high-voltage battery.
See
for the components of a high-voltage
cable.
See
for the connections between high-
voltage batteries.
Inverter
: An inverter converts power from a direct
current (DC) power source (the high-voltage
batteries) to the three phase alternating current
power needed to drive the motor.
Charge Port(s)
: A vehicle may be outfitted with one
or two charging ports. A single coupler in either inlet
may be used to charge a vehicle with dual ports.
When both inlets are used, inlet one charges battery
one and two and inlet two charges battery three and
the power supplied to inlet one is double the power
supplied to inlet two.
Charging
: The high-voltage batteries can only be
charged at DC charging stations meeting the J1772
standards.
Charging Time
: When charging with a direct current,
the charging time will vary based on the size of the
charger and the vehicle limitations. In general,
charging a factory-fitted high-voltage battery to 95%
of the charge level with a direct current and a
charging power of 180kW will take 2-3 hours,
depending on battery size.
Electric Vehicle Distribution Module (EVDM)
: An
electrical system on a commercial vehicle usually
consists of 12V and/or 24V loads/components that
are connected to power distribution modules to get
energized and be functional. In these systems, it is
desirable to protect 12V and 24V components,
outputs/inputs, wires and cables from possible over-
current events. The electric vehicle power distribution
module (EVDM) is the main component implementing
this functionality on an electric vehicle.
The eCascadia has a multiplex electrical system. By
transmitting multiple electronic messages through the
same wire, a multiplex system reduces the number
of interconnected wires, allows for more precise
control of the electrical system, and makes it easer
and quicker to diagnose electrical faults and add
optional equipment.
In addition, the wiring harnesses are developed for
the maximum number of options, meaning that space
for additional wires is available within the wiring
harness regardless of the number of optional
features on the vehicle. This design provides a
cleaner main harness and is meant to eliminate the
need for wiring overlays
Electronic control modules (ECUs) coordinate power
to outputs such as lighting, displays, gauges, and
indicators and control power distribution by
monitoring inputs such as sensors and switches.
The ECUs also continuously monitor the status of all
input devices and transmit messages over multiple
control area networks (CANs), reducing the number
of sensors required for operation.
Electric Vehicle Cooling Components
The cooling components are designed to keep the
eAxles and high-voltage batteries at their optimum
operating temperatures. This results in the most
efficient delivery of power and less component
stress.
The central components of the cooling system are
the radiator assembly, surge tanks, electric
refrigerant compressor, heaters, and the electric
pumps; the pumps circulate the coolant through all of
the connected components.
Radiator
: The radiator is placed in front of the front
box, connecting to the other cooling components. It
helps to eliminate excess heat from the eAxle and
high-voltage batteries. It includes a liquid coolant,
hoses to circulate the coolant, fans and a thermostat
that monitors the coolant temperature.
Electrical System
9.1
Summary of Contents for PX113064S T 2016
Page 4: ......
Page 10: ......
Page 18: ......
Page 58: ......
Page 86: ......
Page 112: ......
Page 122: ......
Page 142: ......
Page 154: ......
Page 155: ...12 Steering System Power Steering System 12 1...
Page 158: ......
Page 159: ...13 eAxle eAxle 2 Speed Transmission 13 1...
Page 176: ......
Page 190: ......
Page 202: ......
Page 222: ......
Page 223: ...20 Emissions Information Noise Emissions 20 1 Greenhouse Gas Emissions 20 1...
Page 229: ......
Page 236: ......