2
MAINTENANCE
LUBRICATION:
Lubricate the bearings with a proper ball
bearing grease through the grease nipples provided. Do
not over lubricate. Ball bearings require a surprisingly small
amount of grease. Over lubrication causes the bearing to
break down because the grease then tends to churn and
produce heat. If this temperature goes above 200°F, it will
break down causing the bearing to fail. Units supplied with
sealed bearings are not equipped with grease nipples, no
maintenance required.
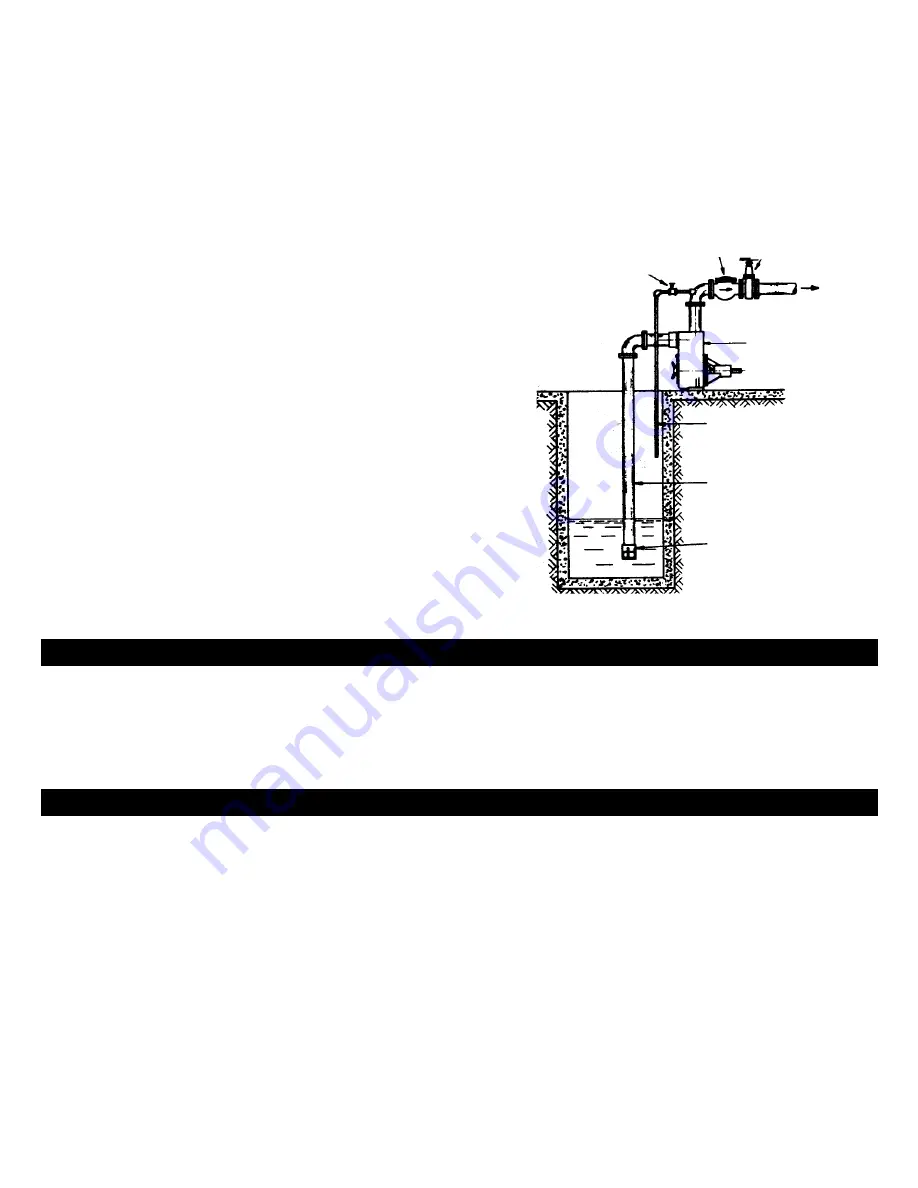
Gate Valve (min. 3/4")
Check Valve
Gate Valve
Discharge
Pump
Air Bleed Line
Suction Pipe
Strainer
FIG. 1
This enables the pump to prime quickly and prevents
kinking or breaks in the hose. In cases where a maximum
volume of water is required over a prolonged period of
time, the suction line should be led horizontally to the
pump.
c) DRAINING:
During freezing temperatures, the pump
should be drained each time it is stopped for any
appreciable length of time. To drain, remove the drain
plug at the bottom of the pump casing and make sure
that the drain hole is not plugged. After all the water has
been drained from the pump casing, the unit should be
operated for a few seconds so that all of the water will be
removed from the impeller.
NOTE:
The pump should also be drained after corrosive
liquids have been pumped.
d) UNCLOGGING:
Should the pump become clogged it can
easily be cleaned out as outlined below.
1) Remove the wing nuts (75).
2) Pry the clean out cover (78) loose with a screwdriver
using the specially fitted lugs on the cover.
3) Remove the cleanout cover.
4) Clean out the interior of the pump making sure the check
valve is also clean.
5) Replace the cleanout cover making sure the O-ring is
clean and in place.
A clogged impeller results in excessive vibration. Should this
occur, the impeller must be cleaned out immediately to avoid
serious damage to the unit.
These pumps offer the added feature of removing the
impeller and seal through the clean out cover for service or
replacement.
REPAIR
TO DISASSEMBLE
(Fig. 2)
:
1. Remove the six nuts (530C) and then remove transmission
head (79).
2. Remove the head bolt (510).
3. Remove impeller (2) by unscrewing it in a counter-
clockwise direction.
4. Slip the rotating seal (90) off the shaft.
5. When replacing stationary seat, remove the adapter
plate (3) from the transmission head and press out the
stationary seat.
TO ASSEMBLE:
1. Clean all parts thoroughly before assembling.
2. Apply liquid soap on rubber cup on stationary seat and
push it into the adapter plate using thumbs only. Make sure
the smooth surface of the ceramic seat faces outwards.
3. Slide the adapter plate over the shaft being very careful
not to damage the stationary seat.
4. Slip the rotating seal onto the shaft with the seal ring
towards the stationary seat.
5. Reassemble the impeller to the shaft.
6. Bolt the transmission head to the pump.
NOTE:
Replacing Parts: When replacing either the body,
wear plate, impeller or shaft, the clearance between the
impeller and the wear plate should be checked. This clear-
ance should be about .020 inches to .035 inches. If it is less,
the impeller will rub against the wear plate causing undue
wear and increase the load. If the clearance is greater, an
increased amount of recirculation will take place causing
a decrease in efficiency and increase priming time. This
tolerance may be achieved by the addition or removal of
gaskets.






























