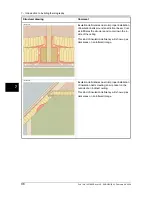
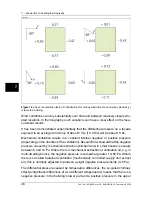
7.3.5
Measuring conditions & measuring season
The foregoing may be summarized as follows as to the requirements with regard to
measuring conditions when carrying out thermographic imaging of buildings.
Thermographic imaging is done in such a way that the disruptive influence from ex-
ternal climatic factors is as slight as possible. The imaging process is therefore carried
out indoors, i.e. where a building is heated, the structure’s warm surfaces are exam-
ined.
Outdoor thermography is only used to obtain reference measurements of larger
façade surfaces. In certain cases, e.g. where the thermal insulation is very bad or
where there is an internal positive pressure, outdoor measurements may be useful.
Even when investigating the effects of installations located within the building’s climatic
envelope, there may be justification for thermographic imaging from outside the
building.
The following conditions are recommended:
■
The air temperature difference within the relevant part of the building must be at
least +10°C (+18°F) for a number of hours before thermographic imaging and for
as long as the procedure takes. For the same period, the ambient temperature
difference must not vary by more than ±30% of the difference when the thermo-
graphic imaging starts. During the thermographic imaging, the indoor ambient
temperature should not change by more than ±2°C (±3.6°F).
■
For a number of hours prior before thermographic imaging and as long as it con-
tinues, no influencing sunlight may fall upon the relevant part of the building.
■
Negative pressure within the structure ≈ 10–50 Pa.
■
When conducting thermographic imaging in order to locate only air leaks in the
building’s enclosing sections, the requirements in terms of measuring conditions
may be lower. A difference of 5°C (9°F) between the inside and outside ambient
temperatures ought to be sufficient for detecting such defects. To be able to detect
air leaks, certain requirements must however be made with regard to the differential
pressure; about 10 Pa should be sufficient.
7.3.6
Interpretation of infrared images
The main purpose of thermography is to locate faults and defects in thermal insulation
in exterior walls and floor structures and to determine their nature and extent. The
measuring task can also be formulated in such a way that the aim of the thermography
is to confirm whether or not the wall examined has the promised insulation and air-
tightness characteristics. The ‘promised thermal insulation characteristics’ for the wall
according to the design can be converted into an expected surface temperature dis-
tribution for the surface under investigation if the measuring conditions at the time
when the measurements are taken are known.
7
Publ. No. 1557882 Rev. a156 – ENGLISH (EN) – February 28, 2006
49
7 – Introduction to building thermography
Summary of Contents for ThermaCAM B2
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 6: ......
Page 7: ...ThermaCAM B2 User s manual Publ No 1557882 Rev a156 ENGLISH EN February 28 2006...
Page 191: ......