8
Festo — CMMT-ST-C8-1C-...-S0 — 2021-04b
Product overview
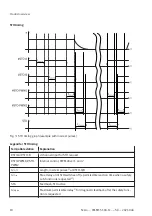
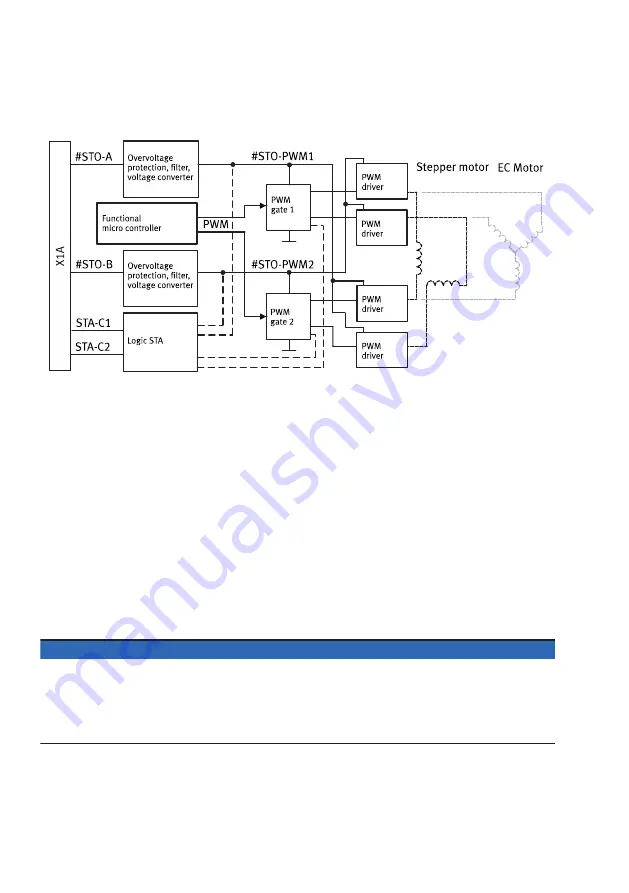
Functional principle of STO
Fig. 2: Functional principle of STO
STO request
The safety sub-function STO is requested on 2 channels by simultaneously switching off the control
voltage at both control inputs #STO-A and #STO-B.
The signals of inputs #STO-A/B are low active, so they are marked with #.
The drive behaves as follows when the safety sub-function STO is requested:
–
Behaviour of the drive with a running motor: the movement of the drive is not decelerated via a
braking ramp. The drive continues to move uncontrolled due to inertia or external forces until it
comes to a standstill by itself.
–
Behaviour of the drive with a stopped motor: the drive is uncontrolled and can be moved by external
forces.
The safe state is achieved after the safety sub-function STO has been requested if all motor coils are
switched off and current cannot flow through them.
NOTICE
Detent movement if the output stage fails.
If the output stage of the device fails when a safety sub-function STO is active, it may result in
the drive jerking with a limited detent movement of the rotor. The maximum rotation angle/travel
corresponds to the pole pitch of the motor used.
• Take this behaviour into account when designing the system's safety function.
After the safety sub-function STO has been requested and the request completed, the functional
controller enable must be activated.
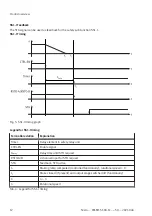
Feedback via diagnostic contact STA
The state of the safety sub-function STO can be reported to the safety relay unit via the diagnostic
contact STA.