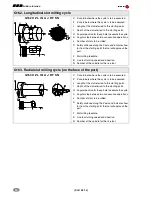
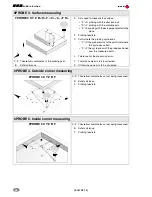
Quick reference
12
(S
OFT
03.1
X
)
G63
*
*
Rigid tapping
G70
*
?
*
Programming in inches
G71
*
?
Programming in millimeters
G72
*
Scaling factor
G73
*
*
Coordinate system rotation (pattern rotation)
G74
*
Home search
G90
*
?
Programming in absolute coordinates
G91
*
?
*
Programming in incremental coordinates
G92
!
*
Coordinate preset
G93
*
*
Machining time in seconds
G94
*
?
Feedrate in millimeters/minute (inches/minute)
G95
*
?
*
Feedrate in millimeters/revolution (inches/revolution)
G96
*
*
Constant surface speed
G97
*
*
Constant turning speed
G100
*
Probing
G101
*
Include probe offset
G102
*
Exclude probe offset
G108
*
*
Feedrate blending at the beginning of the block
G109
*
Feedrate blending at the end of the block
G112
*
Changing of parameter range of an axis
G130
*
*
Percentage of acceleration to be applied per axis
G131
*
*
Percentage of acceleration to be applied to all the axes
G132
*
*
Percentage of jerk to be applied per axis
G133
*
*
Percentage of jerk to be applied to all the axes
G134
*
*
Percentage of Feed-Forward to be applied
G135
*
*
Percentage of AC-Forward to be applied
G136
*
?
*
Circular transition between blocks
G137
*
?
Linear transition between blocks
G138
*
*
Direct activation/cancellation of tool compensation
G139
*
*
Indirect activation/cancellation of tool compensation
G145
*
*
Freezes/resumes tangential control
G151
*
*
*
Programming in diameters
G152
*
Programming in radius
G157
*
*
Excluding axes in the zero offset
G158
*
*
Incremental zero offset
G159
!
*
Additional absolute zero offsets
G170
*
Hirth axes OFF
G171
*
*
Hirth axes ON
G18x
*
OEM subroutines
G192
*
*
Turning speed limit in constant surface speed mode
G193
*
Interpolating the feedrate
G196
*
*
Constant cutting point feedrate
G197
*
*
Constant tool center feedrate
G198
*
Setting of lower software travel limits
G199
*
Setting of upper software travel limits
Function
M
D
V
Meaning
Summary of Contents for CNC 8070
Page 1: ...Quick reference SOFT 03 1X REF 0706 CNC 8070...
Page 44: ......