SPI Flash File System
Up until now, we've always included the HTML for our web pages as string literals in our sketch. This makes our code very hard to
read, and you'll run out of memory rather quickly.
If you remember the introduction, I mentioned the Serial Peripheral Interface Flash File System, or SPIFFS for short. It's a light-weight
file system for microcontrollers with an SPI flash chip. The on-board flash chip of the ESP8266 has plenty of space for your webpages,
especially if you have the 1MB, 2MB or 4MB version.
SPIFFS let's you access the flash memory as if it was a normal file system like the one on your computer (but much simpler of course):
you can read and write files, create folders ...
The easiest way to learn how to use SPIFFS is to look at some examples. But a file server with no files to serve is pretty pointless, so I'll
explain how to upload files to the SPIFFS first.
Uploading files to SPIFFS
To select the right files to upload, you have to place them in a folder called data, inside the sketch folder of your project: Open your
sketch in the Arduino IDE, and hit CTRL+K. Wait for a file explorer window to open, and create a new folder named data. Copy your
files over to this folder. (Only use small files like text files or icons. There's not enough space for large photos or videos.)
Next, select all files in the folder (CTRL+A) and check the size of all files combined (don't forget subfolders). Go to the Arduino IDE
again, and under Tools > Flash Size, select an option with the right flash size for your board, and a SPIFFS size that is larger than the
size of your data folder.
Then upload the sketch. When that's finished, make sure that the Serial Monitor is closed, then open the Tools menu, and click
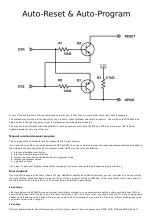
ESP8266 sketch data upload. If your ESP has auto-reset and auto-program, it should work automatically, if you don't have auto-
program, you have to manually enter program mode before uploading the data to SPIFFS. The procedure is exactly the same as
entering program mode before uploading a sketch.
If you get an error saying
SPIFFS_write error(-10001): File system is full
, this means that your files are too large to fit into the SPIFFS
memory. Select a larger SPIFFS size under Tools > Flash Size, or delete some files.
Even if your computer says that the files are smaller than the selected SPIFFS size, you can still get this error: this has to do with block
sizes, and metadata like file and folder names that take up space as well.
If you change the SPIFFS size, you have to reupload your sketch, because when you change the SPIFFS size, the memory location will
be different. The program has to know the updated SPIFFS address offset to be able to read the files.
SPIFFS File Server
The following example is a very basic file server: it just takes the URI of the HTTP request, checks if the URI points to a file in the
SPIFFS, and if it finds the file, it sends it as a response.
#include
<
ESP8266WiFi
.
h
>
#include
<
WiFiClient
.
h
>
#include
<
ESP8266WiFiMulti
.
h
>
#include
<
ESP8266mDNS
.
h
>
#include
<
ESP8266WebServer
.
h
>
#include
<
FS
.
h
>
// Include the SPIFFS library
ESP8266WiFiMulti wifiMulti;
// Create an instance of the ESP8266WiFiMulti class, called 'wifiMulti'
ESP8266WebServer
server(80);
// Create a webserver object that listens for HTTP request on port 80
String
getContentType(
String
filename);
// convert the file extension to the MIME type
bool
handleFileRead(
String
path);
// send the right file to the client (if it exists)
void
setup
() {
Serial
.
begin
(115200);
// Start the Serial communication to send messages to the computer
delay
(10);
Serial
.
println
(
'\n'
);
wifiMulti
.
addAP(
"ssid_from_AP_1"
,
"your_password_for_AP_1"
);
// add Wi-Fi networks you want to connect to
wifiMulti
.
addAP(
"ssid_from_AP_2"
,
"your_password_for_AP_2"
);
wifiMulti
.
addAP(
"ssid_from_AP_3"
,
"your_password_for_AP_3"
);
Serial
.
println
(
"Connecting ..."
);
int
i
=
0;
while
(wifiMulti
.
run
()
!=
WL_CONNECTED) {
// Wait for the Wi-Fi to connect
delay
(250);
Serial
.
(
'.'
);
}
Serial
.
println
(
'\n'
);
Serial
.
(
"Connected to "
);
Serial
.
println
(
WiFi
.
SSID
());
// Tell us what network we're connected to
Serial
.
(
"IP address:\t"
);
Serial
.
println
(
WiFi
.
localIP
());
// Send the IP address of the ESP8266 to the computer
if
(
MDNS
.
begin
(
"esp8266"
)) {
// Start the mDNS responder for esp8266.local
Serial
.
println
(
"mDNS responder started"
);
}
else
{
Serial
.
println
(
"Error setting up MDNS responder!"
);
}
SPIFFS
.
begin
();
// Start the SPI Flash Files System
server
.
onNotFound
([]() {
// If the client requests any URI
if
(
!
handleFileRead(server
.
uri
()))
// send it if it exists
server
.
send
(404
,
"text/plain"
,
"404: Not Found"
);
// otherwise, respond with a 404 (Not Found) error
});
server
.
begin
();
// Actually start the server
Serial
.
println
(
"HTTP server started"
);
}
void
loop
(
void
) {
server
.
handleClient
();
}