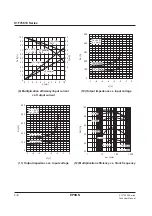
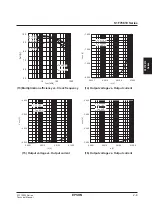
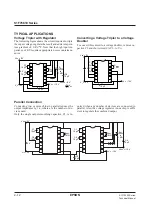
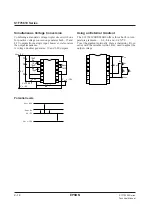
S1F76610 Series
2–4
EPSON
S1F70000 Series
Technical Manual
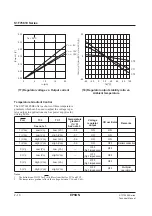
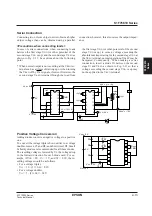
3. R
Lmin
is a function of V
1
Electrical Characteristics
V
DD
= 0V, V
1
= –5V, Ta = –40 to +85
°
C unless otherwise noted
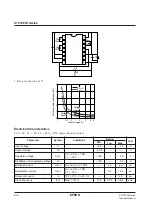
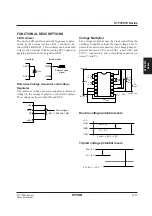
C1
10
µ
F
C2
10
µ
F
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
R
OSC
C
L
R
L
1M
Ω
C3
22
µ
F
D1
+
+
+
5
4
3
2
1
0
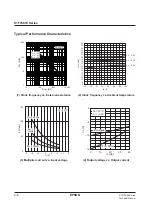
1
Input voltage (V)
Minimum load resistance (k
Ω
)
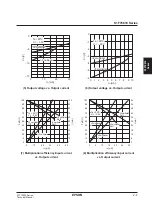
6
5
4
3
2
1.5
V
STA2
V
STA1
Voltage
tripler
Voltage
doubler
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Input voltage
Output voltage
Regulator voltage
Stabilization circuit operating voltage
Multiplier current
Stabilization current
Quiescent current
Clock frequency
V
I
V
O
V
REG
V
O
I
OPR1
I
OPR2
I
Q
f
OSC
R
L
=
∞
, R
RV
= 1M
Ω
,
V
O
= –18V
R
L
=
∞
, R
OSC
= 1M
Ω
R
L
=
∞
, R
RV
= 1M
Ω
,
V
O
= –15V
TC2 = TC1 = V
O
, R
L
=
∞
R
OSC
= 1M
Ω
Rating
Min.
–6.0
–18.0
–18.0
–18.0
—
—
—
16.0
Typ.
—
—
—
—
40
5.0
—
20.0
Max.
–1.8
—
–2.6
–3.2
80
12.0
2.0
24.0
Unit
V
V
V
V
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
kHz