The Switch User’s Guide
by the Switch.
If the Aging Time is too short however, many entries may be aged out too soon. This
will result in a high percentage of received packets whose source addresses cannot
be found in the forwarding table, in which case the switch will broadcast the packet
to all ports, negating many of the benefits of having a switch.
Static forwarding entries are not affected by the aging time.
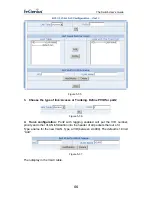
Type the number of seconds that an inactive MAC address remains in the switch’s
address table. The valid range is 30~1,000 seconds. Default is 300 seconds.
Figure 5-47
5.5 QOS
5.5.1 Understand QOS
Quality of Service (QoS) is an advanced traffic prioritization feature that allows you
to establish control over network traffic. QoS enables you to assign various grades
of network service to different types of traffic,
QoS reduces bandwidth limitations, delay, loss, and jitter. It also provides increased
reliability for delivery of your data and allows you to prioritize certain applications
across your network.
You can use QoS on your system to:
z
Classifying traffic based on MAC addres/ 802.1p priority bits/ VLAN/ ports.
z
Improve performance for specific types of traffic and preserve performance as
the amount of traffic grows.
z
Reduce the need to constantly add bandwidth to the network.
z
Manage network congestion.
QoS Terminology
Classifier
-
classifies the traffic on the network. Traffic classifications are
determined by protocol, application, source, destination, and so on. You can create
and modify classifications. The Switch then groups classified traffic in order to
schedule them with the appropriate service level.
DiffServ Code Point (DSCP)
-
is the traffic prioritization bits within an IP header
that are encoded by certain applications and/or devices to indicate the level of
61