9
⅝-11
60 (81)
90 (122)
120 (163)
¾-10
100 (136)
150 (203)
200 (271)
⅞-9
160 (217)
240 (325)
320 (434)
1-8
240 (325)
370 (502)
500 (6-78)
1⅛-8
350 (475)
525 (712)
700 (949)
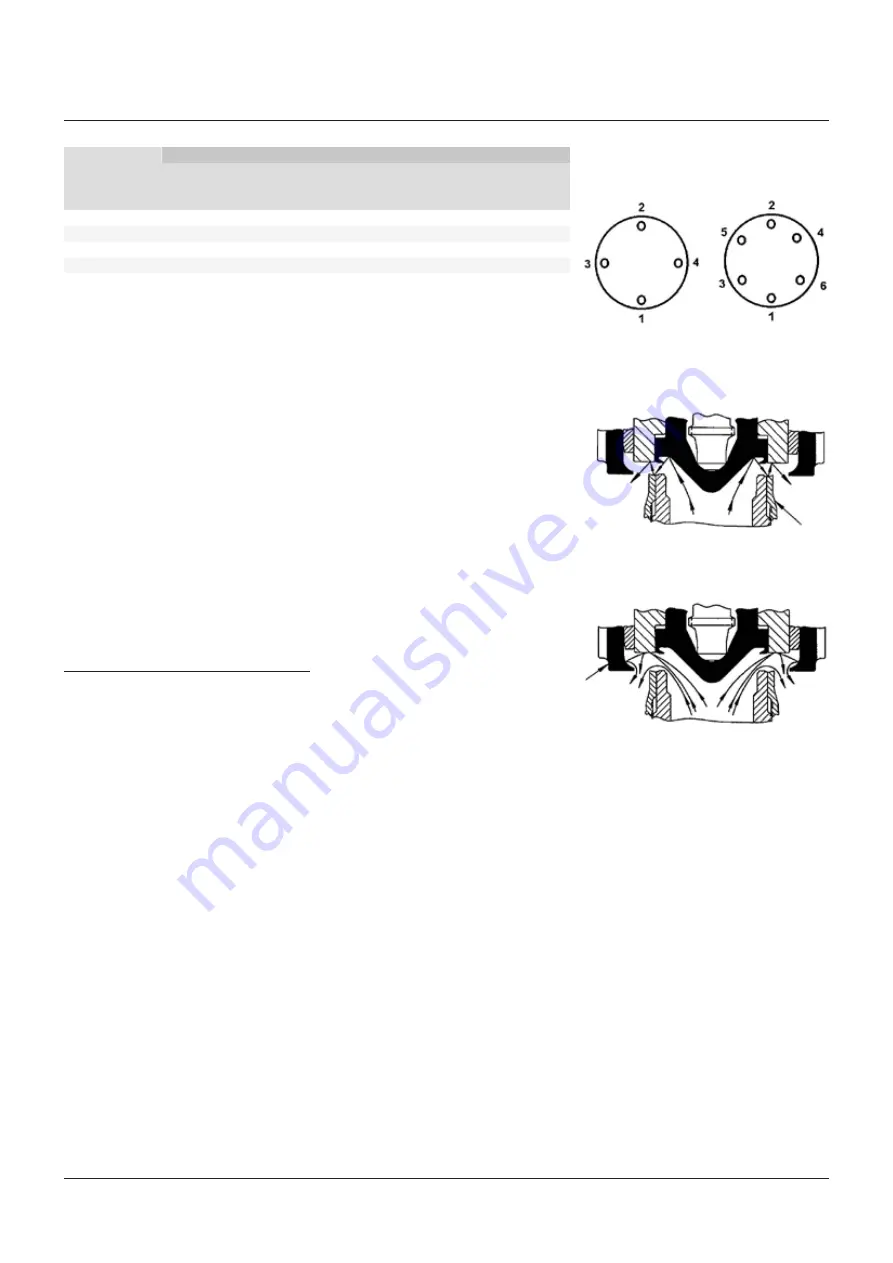
FIGURE 7 - EFFECT OF NOZZLE RING
FIGURE 8 - EFFECT OF GUIDE RING
7 OPERATION
Crosby Style HC/HCA safety valves open with a
sharp pop at the set pressure and remain open,
relieving rated capacity at 3% overpressure.
As inlet pressure decays below the opening
pressure, the safety valve remains open until
a pressure about 4% below the set pressure
is reached. At that point, the safety valve
closes sharply.
Nozzle ring
Guide ring
CROSBY
®
STYLES HC AND HCA ISOFLEX™ SAFETY VALVES
INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTIONS
FIGURE 6 - TIGHTENING OF BONNET AND/OR
COOLING SPOOL STUD NUTS
Stud thread
Torque (ft·lb) (Nm) to produce stress in stud bolts
30.000 psi (2.068 bar)
45.000 psi (3.203 bar)
60.000 psi (4.137 bar)
Stress
Stress
Stress
ft·lb (Nm)
ft·lb (Nm)
ft·lb (Nm)
4 studs
6 studs
NOTES
1. Valve studs and nuts shall be clean and inspected
visually to ensure freedom from any objectionable
foreign matter, rust, burns or physical damage.
2. With the bonnet in place, lubricate the bonnet
studs threads, the nut threads and nut face with
'Never-Seez' compound (which conforms to
Government specification MIL-A-907B, Federal
stock number 803-286-5453) or equivalent.
3. Install nuts on the studs finger-tight.
4. Tighten the nuts in the sequence shown in Figure
6 to approximately one-half the torque value
shown in the table. Repeat the same sequence
of tightening to the torque value shown. Then,
starting with the number 1 nut, tighten each nut in
order in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction
to the value shown in the table above.
5. Wipe off excess lubricant.
Complete the valve assembly with the cap assembly as described in Section 10 - paragraph 'Assembly of cap'
and seal wire the cap set screws.
The sharp opening is produced in two stages.
The initial lift is produced when the steam
pressure under the disc insert (5) exceeds
the spring pressure. To aid in starting the
popping action, steam escapes between the
safety valve seats and is deflected by an angle
on the nozzle ring (3) as shown in Figure 7.
This escaping steam acts on the face of the disc
holder (6) causing an unbalance and the safety
valve pops open. As the disc holder moves
vertically, steam begins to react against the
guide ring (10) and to push the disc holder up
to a high lift as shown in Figure 8. The reaction
of the deflected steam pushes against the
underside of the disc holder and lifts it still
higher on an accumulation of pressure.
As the boiler pressure drops, the safety valve
disc insert (5) settles to a moderate lift and
closes sharply.
The nozzle ring (3) is primarily for ensuring
sharp opening action. Raising the nozzle
ring, bringing it closer to the face of the disc
holder (6), eliminates 'simmer' or 'warn'.
The guide ring (10) is primarily for controlling
blowdown. Raising the guide ring reduces the
reactive pressures against the disc holder and
reduces blowdown. Lowering the guide ring
increases the reactive pressures against the
disc holder and increases the blowdown.



















