Chapter 3
Installation
MAN_105G_1.16
Page 64
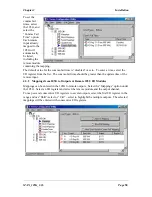
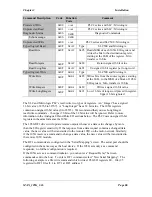
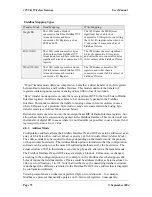
Supported Exception Codes:
Exceptio
n Code
Name
Description
01
Illegal function
The module does not support the function code in the query
02
Illegal data address
The data address received in the query is outside the
initialized memory area
03
Illegal data value
The data in the request is illegal
06
Busy
Unable to process message
4.6.2
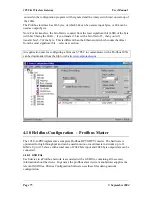
MODBUS Master
If you use the 105G as a Modbus Master, then the host device(s) will be Modbus Slave
device(s). If the RS485 port is used, then multiple Modbus Slave devices can be connected to
the 105G. The 105G Modbus Master will generate Modbus read and write commands to the
Modbus Slave devices.
First read the above section on Modbus Slave operation, for an understanding of how the
105G handles Modbus registers, and the types of Modbus commands the 105G Master can
generate.
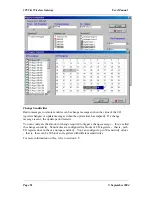
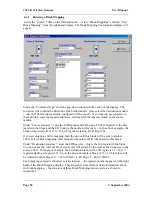
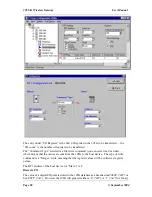
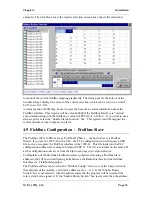
The Modbus Master commands are configured in the “Serial Mapping” screen. The serial
port is configured in the same way as described in the above section on Modbus Slave.
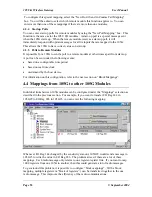
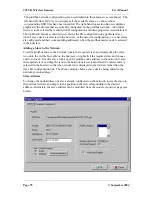
To enter a Modbus command, select “New Serial Mapping”. The following example is a
digital write command which writes 105G I/O registers 20 – 25 (6 registers) to Modbus
outputs 00012 – 00017, at Modbus Slave address 1.
The entry under “I/O Register” is the first I/O register in the 105G to be transferred - the
“I/O count” is the number of registers to be transferred. If the selected Modbus slave does
not respond to the command, then the 105G will write a ‘FFFF’ value to one of its own
registers, configured under “CF Register” - in this case it is register 4800.
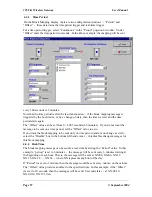
The “Command Type” selected is a write command (you can select read or write) - which
means that the values are sent from the 105G to the Modbus Slave. The type of write
command is a “Digital” write, meaning that the register values will be written as
digital/binary values”.