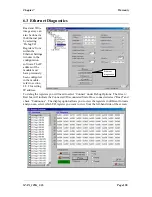
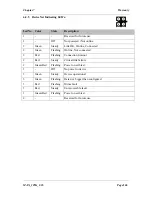
Appendix 2
MAN_105G_1.16
Page 152
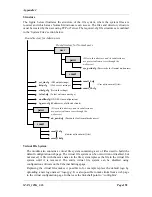
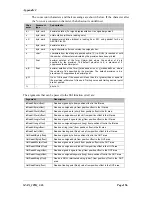
Structure
The figure below illustrates the structure of the file system, where the system files are
located, and which areas Normal/Admin users can access. The files and directory structure
must be created by the user using FTP or Telnet. The required .cfg file structures are outlined
in the ‘System Files’ section below.
Virtual File System
The module also contains a virtual file system containing a set of files used to build the
default configuration webpage. The virtual file system can be overwritten or disabled, but
not erased; A file with the same name in the file system replaces the file in the virtual file
system until it is removed. The entire virtual file system can be disabled using
configuration software on the Ethernet Settings page.
Replacing the virtual files makes it possible to for example replace the default logo by
uploading a new logo named ‘\logo.jpg’. It is also possible to make links from a web page
to the virtual configuration page. In that case the link shall point to ‘\config.htm’.
http.cfg
(Web server settings)
pswd
user
pswd
ssi_str.cfg
(SSI output strings)
ethcfg.cfg
(Network settings)
telwel.cfg
(Telnet welcome message)
onoffln.cfg
(ON/OFF-line configuration)
ip_accs.cfg
(IP addresses of allowed clients)
Root directory for Admin users
Root directory for Normal users
(Files in this directory and its subdirectories
are protected from access through the
webserver)
sys_pswd.cfg
(Passwords for Normal mode users)
email_1.cfg
email_10.cfg
(User defined email files)
(Files in this directory and its subdirectories
are protected from access through the
webserver)
ad_pswd.cfg
(Passwords for Normal mode users)
email_1.cfg
email_10.cfg
(Adminr defined email files)