- 55 -
Disturbances
12.2.3
Error Register
Each of the two sensor channels contains an error register that simplifies the error search. The content of the
error register is transmitted outside via the interface (
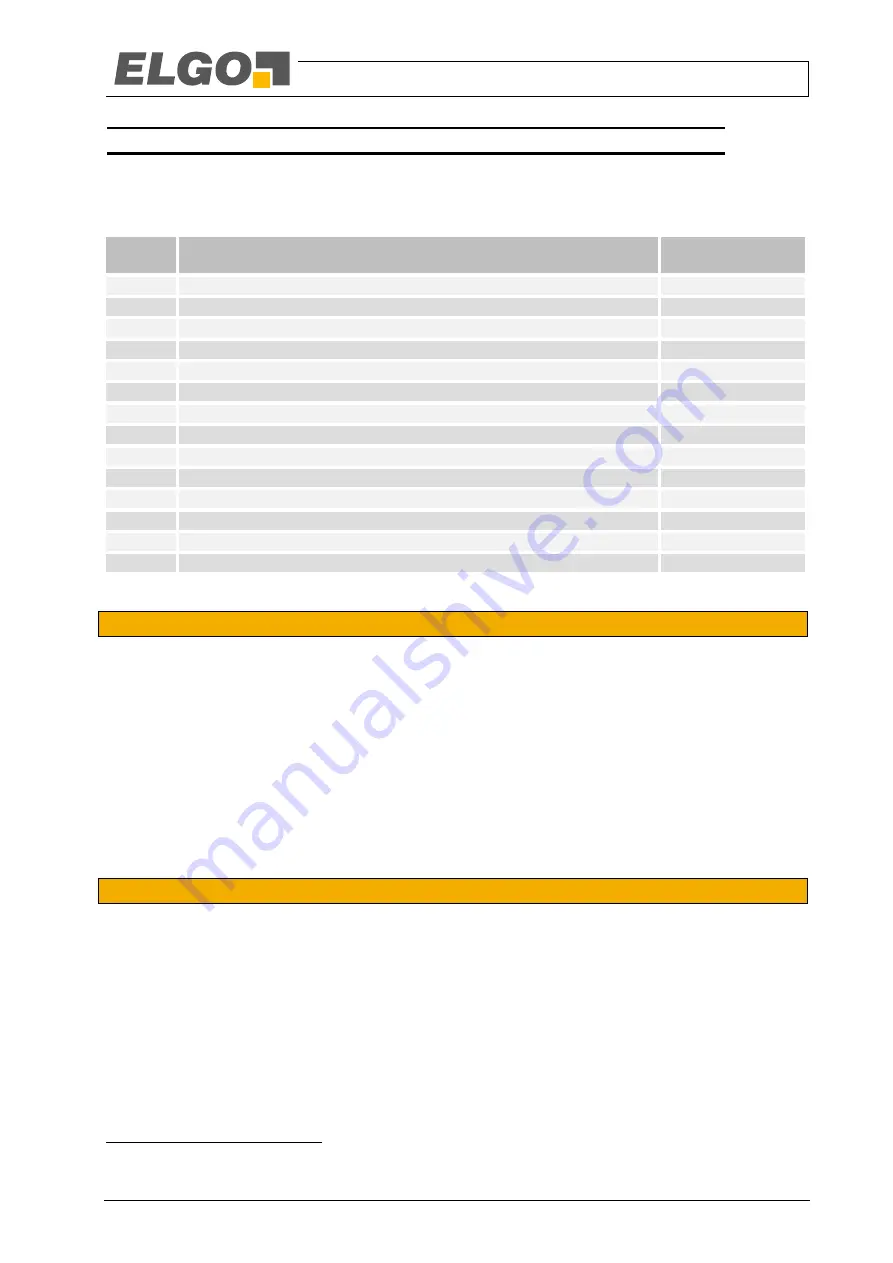
Table 9: Content Error Register
Bit
Problem
Error requires safe
state
0
Overvoltage or undervoltage in general
Yes
1 … 6 Error in voltage monitoring
Yes
7
Error position interpolation
Yes
8 … 12 Internal communication error
Yes
13 … 14 Synchronisation error
Yes
15
EEPROM error
No
1
16
Not used
-
17
Comparing of position between the two channels failed
Yes
18
Communication test failed
Yes
19
Extrapolation not allowed anymore. Too many position jumps occurred
Yes
20
Timeout in the non-safety-relevant processing
No
21
Overvoltage 24V
Yes
22
Undervoltage 24V
Yes
2
23 … 31 Not used
-
12.3
Severe Errors
If one channel detects a severe fault in the processor system (memory error, CPU-error, no communication with
the other channel), its firmware goes into a separate emergency loop and the processors are therefore purpose-
fully blocked. The external interface is not served anymore in this case. This mode is never reset if a voltage is
applied, no matter if normal or battery supply.
There is one exception for channel A to the reaction described above: when there is no communication with the
other channel and the normal supply voltage has a strong undervoltage and therefore channel A is in single-
channel operation. This means that channel B is deliberately switched off (
9.2.2 Single-Channel Operation).
Under this condition, channel A continues to send its positions and sets the relevant status bit (section
Status Bits
in the chapter of the relevant interface
9.5.4). When the voltage returns and all error detection measures
operate in their entirety in both channels, LIMAX44 RED returns to normal operation (
12.4
Informative Errors (not Safety-Relevant)
The two chapters 12.2 and 12.3 mainly treated errors in the safety-relevant processing which require the transi-
tion into safe state; either explicitly by sending the request for transition into safe state or implicitly due to missing
messages which cause a timeout in the evaluation unit.
In order to avoid non-safety-relevant operational elements influencing this behaviour, some information of a
purely informative character are exempted from the request for transition into safe state. Those errors can only
be identified over the error register (
12.2.3. Informative errors are also signalled via the error LED. Namely
these are errors in the EEPROM and timeout in the non-safety-relevant processing.
1
The EEPROM only contains the non-safety-relevant floor table for the indication of the door zones.
2
An undervoltage of the 24 V implicitly requests a transition into the safe state because in this case the second channel is
switched off in order to save energy and only a non-safe position is transmitted.
























