© ElectroCraft 2022
43
CPP-x06V48A-SA-CAN Drive User Manual
WARNING!
Installing capacitance value lesser than 50
μF per each ampere deceleration current could result in an
overvoltage fault condition and may result in damage to the drive.
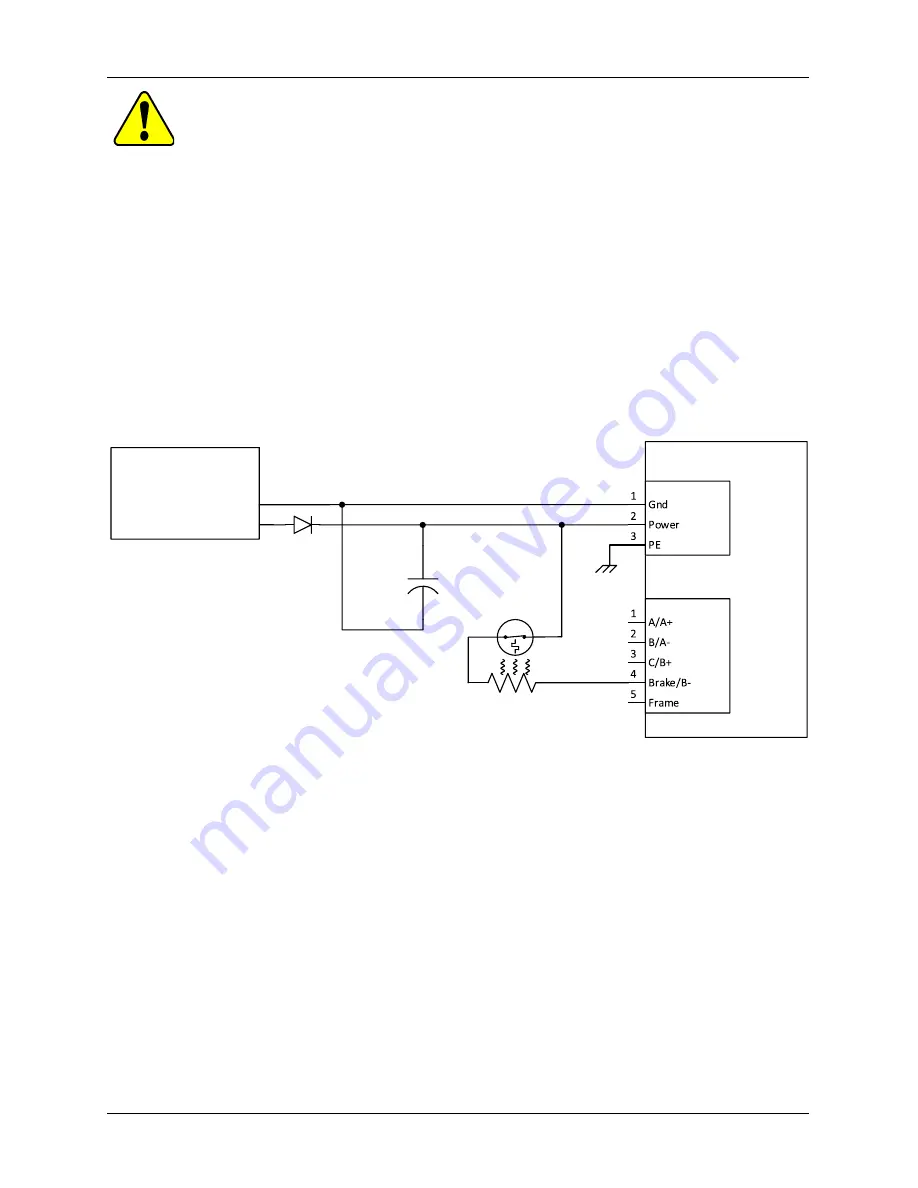
13.5 Connecting External Brake Resistor and Bulk Capacitor
The braking resistor and bulk capacitor wiring is shown in Figure 33.
Temperature Sensitive Device Connection:
The user supplied temperature sensitive device is connected
in series with the brake resistor as shown in Figure 33. Generally, the temperature sensitive device
should be mounted in contact with the surface of the brake resistor or very close to it for an effective
operation.
Optional Diode connection:
Adding a diode between the positive terminal of the power supply and J1 pin
2 of the drive as shown in Figure 33 will protect the power supply from any back fed overvoltage while
braking. The diode is sized by the application’s maximum reverse voltage and forward current.
Drive
J2
J1
+DC Power
-DC Power
DC Power
Supply
+
Bulk
Capacitor
Diode
Brake
Resistor
Temperature
Sensitive Device
Figure 35: External brake resistor and bulk capacitor connection to the drive
The ElectroCraft Braking Module is designed for this purpose and is compatible with CPP-x06V48A-SA-
CAN. Refer section 13.6 for application information.



















